Could Biomarkers Direct Therapy for the Septic Patient?
- PMID: 26857961
- PMCID: PMC4851319
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.115.230797
Could Biomarkers Direct Therapy for the Septic Patient?
Abstract
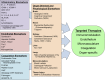
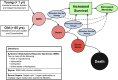
Sepsis is a serious medical condition caused by a severe systemic inflammatory response to a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection that most commonly affects neonates and the elderly. Advances in understanding the pathophysiology of sepsis have resulted in guidelines for care that have helped reduce the risk of dying from sepsis for both children and older adults. Still, over the past three decades, a large number of clinical trials have been undertaken to evaluate pharmacological agents for sepsis. Unfortunately, all of these trials have failed, with the use of some agents even shown to be harmful. One key issue in these trials was the heterogeneity of the patient population that participated. What has emerged is the need to target therapeutic interventions to the specific patient's underlying pathophysiological processes, rather than looking for a universal therapy that would be effective in a "typical" septic patient, who does not exist. This review supports the concept that identification of the right biomarkers that can direct therapy and provide timely feedback on its effectiveness will enable critical care physicians to decrease mortality of patients with sepsis and improve the quality of life of survivors.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond sepsis pathophysiology with cytokines: what is their value as biomarkers for disease severity?Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2005 Mar;100 Suppl 1:217-21. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762005000900037. Epub 2005 Jun 14. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2005. PMID: 15962126 Review.
-
Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012.Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580-637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23353941
-
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Research Priorities for Sepsis and Septic Shock.Crit Care Med. 2018 Aug;46(8):1334-1356. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003225. Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29957716
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
Cited by
-
Biomarkers Predicting Tissue Pharmacokinetics of Antimicrobials in Sepsis: A Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 May;61(5):593-617. doi: 10.1007/s40262-021-01102-1. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35218003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical phenotypes of acute kidney injury are associated with unique outcomes in critically ill septic children.Pediatr Res. 2021 Nov;90(5):1031-1038. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01363-3. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Pediatr Res. 2021. PMID: 33531676 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation Management? Orienting Sepsis R&D and Technology Transfer Towards Stratified Medicine.EBioMedicine. 2016 Apr;6:8-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 10. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27211534 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Detection of Early Cytokine Storm in Patients with Septic Shock After Abdominal Surgery.J Transl Int Med. 2020 Jun 30;8(2):91-98. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2020-0014. eCollection 2020 Jun. J Transl Int Med. 2020. PMID: 32983931 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics as a Driver in Advancing Precision Medicine in Sepsis.Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Sep;37(9):1023-1032. doi: 10.1002/phar.1974. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Pharmacotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28632924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham E, Reinhart K, Opal S, Demeyer I, Doig C, Rodriguez AL, Beale R, Svoboda P, Laterre PF, Simon S, et al. OPTIMIST Trial Study Group (2003) Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290:238–247. - PubMed
-
- Adam N, Kandelman S, Mantz J, Chrétien F, Sharshar T. (2013) Sepsis-induced brain dysfunction. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 11:211–221. - PubMed
-
- Adkins B, Leclerc C, Marshall-Clarke S. (2004) Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol 4:553–564. - PubMed
-
- Alhamdi Y, Abrams ST, Cheng Z, Jing S, Su D, Liu Z, Lane S, Welters I, Wang G, Toh CH. (2015) Circulating histones are major mediators of cardiac injury in patients with sepsis. Crit Care Med 43:2094–2103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

