Loss of the transcription factor Meis1 prevents sympathetic neurons target-field innervation and increases susceptibility to sudden cardiac death
- PMID: 26857994
- PMCID: PMC4760953
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.11627
Loss of the transcription factor Meis1 prevents sympathetic neurons target-field innervation and increases susceptibility to sudden cardiac death
Abstract
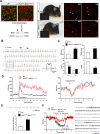
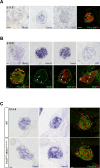
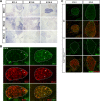
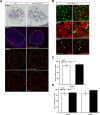
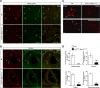
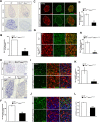
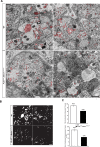
Although cardio-vascular incidents and sudden cardiac death (SCD) are among the leading causes of premature death in the general population, the origins remain unidentified in many cases. Genome-wide association studies have identified Meis1 as a risk factor for SCD. We report that Meis1 inactivation in the mouse neural crest leads to an altered sympatho-vagal regulation of cardiac rhythmicity in adults characterized by a chronotropic incompetence and cardiac conduction defects, thus increasing the susceptibility to SCD. We demonstrated that Meis1 is a major regulator of sympathetic target-field innervation and that Meis1 deficient sympathetic neurons die by apoptosis from early embryonic stages to perinatal stages. In addition, we showed that Meis1 regulates the transcription of key molecules necessary for the endosomal machinery. Accordingly, the traffic of Rab5(+) endosomes is severely altered in Meis1-inactivated sympathetic neurons. These results suggest that Meis1 interacts with various trophic factors signaling pathways during postmitotic neurons differentiation.
Keywords: Homeodomain; arrhythmia; cardiac conduction; cell biology; clathrin; developmental biology; endocytosis; mouse; neurotrophin; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Meis1 coordinates a network of genes implicated in eye development and microphthalmia.Development. 2015 Sep 1;142(17):3009-20. doi: 10.1242/dev.122176. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Development. 2015. PMID: 26253404
-
The homeodomain protein Meis1 is essential for definitive hematopoiesis and vascular patterning in the mouse embryo.Dev Biol. 2005 Apr 15;280(2):307-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.01.004. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15882575
-
Dynamic expression of MEIS1 homeoprotein in E14.5 forebrain and differentiated forebrain-derived neural stem cells.Ann Anat. 2013 Oct;195(5):431-40. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 10. Ann Anat. 2013. PMID: 23756022
-
Defects in cardiac conduction system lineages and malignant arrhythmias: developmental pathways and disease.Novartis Found Symp. 2003;250:260-70; discussion 271-5, 276-9. Novartis Found Symp. 2003. PMID: 12956335 Review.
-
Common genetic variation modulating cardiac ECG parameters and susceptibility to sudden cardiac death.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Mar;52(3):620-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.12.014. Epub 2012 Jan 8. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22248531 Review.
Cited by
-
DIVERSITY in binding, regulation, and evolution revealed from high-throughput ChIP.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Apr 23;14(4):e1006090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006090. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29684008 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor Meis1 act as a new regulator of ischemic arrhythmias in mice.J Adv Res. 2022 Jul;39:275-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.11.004. Epub 2021 Nov 15. J Adv Res. 2022. PMID: 35777912 Free PMC article.
-
Restless legs syndrome.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Nov 3;7(1):80. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00311-z. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021. PMID: 34732752 Review.
-
Homeobox gene Meis1 modulates cardiovascular regeneration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Apr;100:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.10.003. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31623926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of single neurons reprogrammed by pancreatic cancer.Nature. 2025 Apr;640(8060):1042-1051. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08735-3. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39961335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Berger AC, Cohen RJ. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science . 1981;213:220–222. - PubMed
-
- Ando M, Totani Y, Walldorf U, Furukubo-Tokunaga K. TALE-class homeodomain transcription factors, homothorax and extradenticle, control dendritic and axonal targeting of olfactory projection neurons in the drosophila brain. Developmental Biology. 2011;358:122–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andres R, Forgie A, Wyatt S, Chen Q, de Sauvage FJ, Davies AM. Multiple effects of artemin on sympathetic neurone generation, survival and growth. Development. 2001;128:3685–3695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

