Distinct Contributions of Enzymic Functional Groups to the 2',3'-Cyclic Phosphodiesterase, 3'-Phosphate Guanylylation, and 3'-ppG/5'-OH Ligation Steps of the Escherichia coli RtcB Nucleic Acid Splicing Pathway
- PMID: 26858100
- PMCID: PMC4859591
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00913-15
Distinct Contributions of Enzymic Functional Groups to the 2',3'-Cyclic Phosphodiesterase, 3'-Phosphate Guanylylation, and 3'-ppG/5'-OH Ligation Steps of the Escherichia coli RtcB Nucleic Acid Splicing Pathway
Abstract
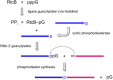
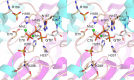
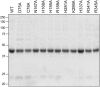
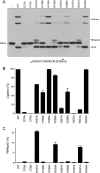
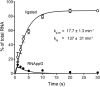
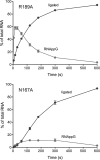
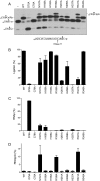
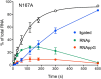
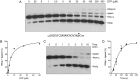
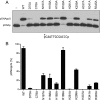
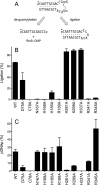
Escherichia coli RtcB is a founding member of a family of manganese-dependent RNA repair enzymes that join RNA 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate (RNA>p) or RNA 3′-phosphate (RNAp) ends to 5′-OH RNA (HORNA) ends in a multistep pathway whereby RtcB (i) hydrolyzes RNA>p to RNAp, (ii) transfers GMP from GTP to RNAp to form to RNAppG, and (iii) directs the attack of 5′-OH on RNAppG to form a 3′-5′ phosphodiester splice junction. The crystal structure of the homologous archaeal RtcB enzyme revealed an active site with two closely spaced manganese ions, Mn1 and Mn2, that interact with the GTP phosphates. By studying the reactions of wild-type E. coli RtcB and RtcB alanine mutants with 3′-phosphate-, 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate-, and 3′-ppG-terminated substrates, we found that enzymic constituents of the two metal coordination complexes (Cys78, His185, and His281 for Mn1 and Asp75, Cys78, and His168 for Mn2 in E. coli RtcB) play distinct catalytic roles. For example, whereas the C78A mutation abolished all steps assayed, the D75A mutation allowed cyclic phosphodiester hydrolysis but crippled 3′-phosphate guanylylation, and the H281A mutant was impaired in overall HORNAp and HORNA>p ligation but was able to seal a preguanylylated substrate. The archaeal counterpart of E. coli RtcB Arg189 coordinates a sulfate anion construed to mimic the position of an RNA phosphate. We propose that Arg189 coordinates a phosphodiester at the 5′-OH end, based on our findings that the R189A mutation slowed the step of RNAppG/HORNA sealing by a factor of 200 compared to that with wild-type RtcB while decreasing the rate of RNAppG formation by only 3-fold.
Importance: RtcB enzymes comprise a widely distributed family of manganese- and GTP-dependent RNA repair enzymes that ligate 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate ends to 5′-OH ends via RNA 3′-phosphate and RNA(3′)pp(5′)G intermediates. The RtcB active site includes two adjacent manganese ions that engage the GTP phosphates. Alanine scanning of Escherichia coli RtcB reveals distinct contributions of metal-binding residues Cys78, Asp75, and His281 at different steps of the RtcB pathway. The RNA contacts of RtcB are uncharted. Mutagenesis implicates Arg189 in engaging the 5′-OH RNA end.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel mechanism of RNA repair by RtcB via sequential 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase and 3'-Phosphate/5'-hydroxyl ligation reactions.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43134-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.302133. Epub 2011 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22045815 Free PMC article.
-
The sequential 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase and 3'-phosphate/5'-OH ligation steps of the RtcB RNA splicing pathway are GTP-dependent.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8558-67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks558. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22730297 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanistic insights into guanylylation of RNA-splicing ligase RtcB joining RNA between 3'-terminal phosphate and 5'-OH.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 18;109(38):15235-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213795109. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22949672 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the structure and function of the RNA ligase RtcB.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Nov 7;80(12):352. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05001-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37935993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA 3'-terminal phosphate cyclases and cyclase-like proteins.Postepy Biochem. 2016;62(3):327-334. Postepy Biochem. 2016. PMID: 28132487 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Sequential rescue and repair of stalled and damaged ribosome by bacterial PrfH and RtcB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 19;119(29):e2202464119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202464119. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35858322 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of 3'-PO4/5'-OH RNA ligase RtcB in complex with a 5'-OH oligonucleotide.RNA. 2021 Feb 22;27(5):584-90. doi: 10.1261/rna.078692.121. Online ahead of print. RNA. 2021. PMID: 33619169 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic structures of the RNA end-healing 5'-OH kinase and 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase domains of fungal tRNA ligase: conformational switches in the kinase upon binding of the GTP phosphate donor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 16;47(22):11826-11838. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1049. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31722405 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular architecture of the human tRNA ligase complex.Elife. 2021 Dec 2;10:e71656. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71656. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34854379 Free PMC article.
-
Ligation of 2', 3'-cyclic phosphate RNAs for the identification of microRNA binding sites.FEBS Lett. 2021 Jan;595(2):230-240. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13976. Epub 2020 Nov 16. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33113149 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

