Agreement of treatment effects for mortality from routinely collected data and subsequent randomized trials: meta-epidemiological survey
- PMID: 26858277
- PMCID: PMC4772787
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.i493
Agreement of treatment effects for mortality from routinely collected data and subsequent randomized trials: meta-epidemiological survey
Erratum in
-
Correction notice to paper "Agreement of treatment effects for mortality from routinely collected data and subsequent randomized trials: meta-epidemiological survey".BMJ. 2018 Aug 17;362:k3210. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k3210. BMJ. 2018. PMID: 30120145 No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To assess differences in estimated treatment effects for mortality between observational studies with routinely collected health data (RCD; that are published before trials are available) and subsequent evidence from randomized controlled trials on the same clinical question.
Design: Meta-epidemiological survey.
Data sources: PubMed searched up to November 2014.
Methods: Eligible RCD studies were published up to 2010 that used propensity scores to address confounding bias and reported comparative effects of interventions for mortality. The analysis included only RCD studies conducted before any trial was published on the same topic. The direction of treatment effects, confidence intervals, and effect sizes (odds ratios) were compared between RCD studies and randomized controlled trials. The relative odds ratio (that is, the summary odds ratio of trial(s) divided by the RCD study estimate) and the summary relative odds ratio were calculated across all pairs of RCD studies and trials. A summary relative odds ratio greater than one indicates that RCD studies gave more favorable mortality results.
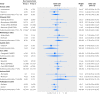
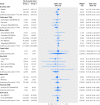
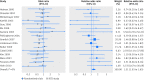
Results: The evaluation included 16 eligible RCD studies, and 36 subsequent published randomized controlled trials investigating the same clinical questions (with 17,275 patients and 835 deaths). Trials were published a median of three years after the corresponding RCD study. For five (31%) of the 16 clinical questions, the direction of treatment effects differed between RCD studies and trials. Confidence intervals in nine (56%) RCD studies did not include the RCT effect estimate. Overall, RCD studies showed significantly more favorable mortality estimates by 31% than subsequent trials (summary relative odds ratio 1.31 (95% confidence interval 1.03 to 1.65; I(2)=0%)).
Conclusions: Studies of routinely collected health data could give different answers from subsequent randomized controlled trials on the same clinical questions, and may substantially overestimate treatment effects. Caution is needed to prevent misguided clinical decision making.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
Comment in
-
Authors' reply to Pérol and colleagues.BMJ. 2016 Dec 16;355:i6747. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i6747. BMJ. 2016. PMID: 27986652 No abstract available.
-
Routinely collected data may usefully supplement randomised controlled data on treatment effects for mortality.BMJ. 2016 Dec 16;355:i6745. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i6745. BMJ. 2016. PMID: 27986716 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Treatment effects in randomised trials using routinely collected data for outcome assessment versus traditional trials: meta-research study.BMJ. 2021 Mar 3;372:n450. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n450. BMJ. 2021. PMID: 33658187 Free PMC article.
-
Current use of routinely collected health data to complement randomized controlled trials: a meta-epidemiological survey.CMAJ Open. 2016 Apr 6;4(2):E132-40. doi: 10.9778/cmajo.20150036. eCollection 2016 Apr-Jun. CMAJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27398355 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Nonrandomized studies using causal-modeling may give different answers than RCTs: a meta-epidemiological study.J Clin Epidemiol. 2020 Feb;118:29-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.10.012. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 31704350 Review.
-
Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of influenza.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 24;2(2):CD010406. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010406.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30798570 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation for acute asthma in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Sep 30;9(9):CD012067. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012067.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 2;10:CD012067. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012067.pub3. PMID: 27687114 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
Quality of observational studies of clinical interventions: a meta-epidemiological review.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022 Dec 7;22(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12874-022-01797-1. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022. PMID: 36476329 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Emulating a Novel Clinical Trial Using Existing Observational Data. Predicting Results of the PreVent Study.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Aug;16(8):998-1007. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201903-241OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019. PMID: 31038996 Free PMC article.
-
An empirical comparison of the harmful effects for randomized controlled trials and non-randomized studies of interventions.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 21;14:1064567. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1064567. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37025494 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation for acute asthma in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 2;10(10):CD012067. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012067.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39356050
References
-
- Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB. Reducing bias in observational studies using subclassification on the propensity score. J Am Stat Assoc 1984;79:516-24. 10.1080/01621459.1984.10478078. . - DOI
-
- Johnson ML, Crown W, Martin BC, Dormuth CR, Siebert U. Good research practices for comparative effectiveness research: analytic methods to improve causal inference from nonrandomized studies of treatment effects using secondary data sources: the ISPOR good research practices for retrospective database analysis task force report—Part III. Value Health 2009;12:1062-73. 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00602.x. .19793071. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
