Final Results of the Sunbelt Melanoma Trial: A Multi-Institutional Prospective Randomized Phase III Study Evaluating the Role of Adjuvant High-Dose Interferon Alfa-2b and Completion Lymph Node Dissection for Patients Staged by Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
- PMID: 26858331
- PMCID: PMC5321066
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.3776
Final Results of the Sunbelt Melanoma Trial: A Multi-Institutional Prospective Randomized Phase III Study Evaluating the Role of Adjuvant High-Dose Interferon Alfa-2b and Completion Lymph Node Dissection for Patients Staged by Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Abstract
Purpose: The Sunbelt Melanoma Trial is a prospective randomized trial evaluating the role of high-dose interferon alfa-2b therapy (HDI) or completion lymph node dissection (CLND) for patients with melanoma staged by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy.
Patients and methods: Patients were eligible if they were age 18 to 70 years with primary cutaneous melanoma ≥ 1.0 mm Breslow thickness and underwent SLN biopsy. In Protocol A, patients with a single tumor-positive lymph node after SLN biopsy underwent CLND and were randomly assigned to observation versus HDI. In Protocol B, patients with tumor-negative SLN by standard histopathology and immunohistochemistry underwent molecular staging by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Patients positive by RT-PCR were randomly assigned to observation versus CLND versus CLND+HDI. Primary end points were disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
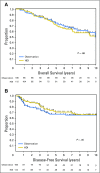
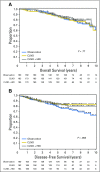
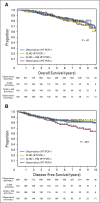
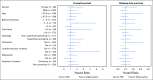
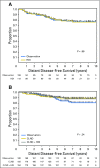
Results: In the Protocol A intention-to-treat analysis, there were no significant differences in DFS (hazard ratio, 0.82; P = .45) or OS (hazard ratio, 1.10; P = .68) for patients randomly assigned to HDI versus observation. In the Protocol B intention-to-treat analysis, there were no significant differences in overall DFS (P = .069) or OS (P = .77) across the three randomized treatment arms. Similarly, efficacy analysis (excluding patients who did not receive the assigned treatment) did not demonstrate significant differences in DFS or OS in Protocol A or Protocol B. Median follow-up time was 71 months.
Conclusion: No survival benefit for adjuvant HDI in patients with a single positive SLN was found. Among patients with tumor-negative SLN by conventional pathology but with melanoma detected in the SLN by RT-PCR, there was no OS benefit for CLND or CLND+HDI.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures
References
-
- Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, et al. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:7–17. - PubMed
-
- McMasters KM, Noyes RD, Reintgen DS, et al. Sunbelt Melanoma Trial Lessons learned from the Sunbelt Melanoma Trial. J Surg Oncol. 2004;86:212–223. - PubMed
-
- Scoggins CR, Ross MI, Reintgen DS, et al. Prospective multi-institutional study of reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for molecular staging of melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2849–2857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

