Prodigiosin Induces Autolysins in Actively Grown Bacillus subtilis Cells
- PMID: 26858704
- PMCID: PMC4729933
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00027
Prodigiosin Induces Autolysins in Actively Grown Bacillus subtilis Cells
Abstract
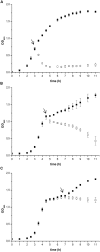
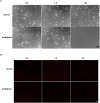
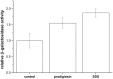
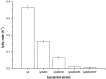
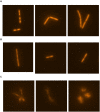
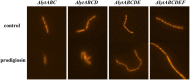
Prodigiosin produced by marine bacterium Vibrio ruber DSM 14379 exhibits a potent antimicrobial activity against a broad range of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The mechanism of prodigiosin antimicrobial action, however, is not known. In this work, the effect of prodigiosin on Bacillus subtilis growth, cell membrane leakage, and induction of autolysins was studied. Treating B. subtilis with prodigiosin resulted in rapid decline of optical density and increased cell membrane leakage measured by β-galactosidase activity. Cell lysis was initiated immediately after treatment with prodigiosin in the middle exponential phase and was completed within 2 h. Lytic activity of prodigiosin in mutant strains with impaired autolysin genes lytABCD decreased for 80% compared to the wild type strain, while in lytABCDEF mutant strain prodigiosin had no bacteriolytic but only bacteriostatic effect. Fast prodigiosin lytic activity on individual B. subtilis cells was confirmed by a modified comet assay. The results indicate that prodigiosin autolysin induction in B. subtilis is growth phase dependent.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; antimicrobial; autolysin; autolysis; comet assay; lytic rate; mechanism; prodigiosin.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

