Phenylpropanoids Accumulation in Eggplant Fruit: Characterization of Biosynthetic Genes and Regulation by a MYB Transcription Factor
- PMID: 26858726
- PMCID: PMC4729908
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01233
Phenylpropanoids Accumulation in Eggplant Fruit: Characterization of Biosynthetic Genes and Regulation by a MYB Transcription Factor
Abstract
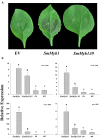
Phenylpropanoids are major secondary metabolites in eggplant (Solanum melongena) fruits. Chlorogenic acid (CGA) accounts for 70-90% of total phenolics in flesh tissues, while anthocyanins are mainly present in the fruit skin. As a contribution to the understanding of the peculiar accumulation of these health-promoting metabolites in eggplant, we report on metabolite abundance, regulation of CGA and anthocyanin biosynthesis, and characterization of candidate CGA biosynthetic genes in S. melongena. Higher contents of CGA, Delphinidin 3-rutinoside, and rutin were found in eggplant fruits compared to other tissues, associated to an elevated transcript abundance of structural genes such as PAL, HQT, DFR, and ANS, suggesting that active in situ biosynthesis contributes to anthocyanin and CGA accumulation in fruit tissues. Putative orthologs of the two CGA biosynthetic genes PAL and HQT, as well as a variant of a MYB1 transcription factor showing identity with group six MYBs, were isolated from an Occidental S. melongena traditional variety and demonstrated to differ from published sequences from Asiatic varieties. In silico analysis of the isolated SmPAL1, SmHQT1, SmANS, and SmMyb1 promoters revealed the presence of several Myb regulatory elements for the biosynthetic genes and unique elements for the TF, suggesting its involvement in other physiological roles beside phenylpropanoid biosynthesis regulation. Transient overexpression in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves of SmMyb1 and of a C-terminal SmMyb1 truncated form (SmMyb1Δ9) resulted in anthocyanin accumulation only of SmMyb1 agro-infiltrated leaves. A yeast two-hybrid assay confirmed the interaction of both SmMyb1 and SmMyb1Δ9 with an anthocyanin-related potato bHLH1 TF. Interestingly, a doubled amount of CGA was detected in both SmMyb1 and SmMyb1Δ9 agro-infiltrated leaves, thus suggesting that the N-terminal region of SmMyb1 is sufficient to activate its synthesis. These data suggest that a deletion of the C-terminal region of SmMyb1 does not limit its capability to regulate CGA accumulation, but impairs anthocyanin biosynthesis. To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting a functional elucidation of the role of the C-term conserved domain in MYB activator proteins.
Keywords: RACE; S. melongena; chlorogenic acid; gene regulation; genome walking; qRT-PCR.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

