Class-Specific Evolution and Transcriptional Differentiation of 14-3-3 Family Members in Mesohexaploid Brassica rapa
- PMID: 26858736
- PMCID: PMC4726770
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00012
Class-Specific Evolution and Transcriptional Differentiation of 14-3-3 Family Members in Mesohexaploid Brassica rapa
Abstract
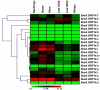
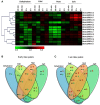
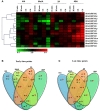
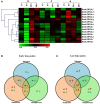
14-3-3s are highly conserved, multigene family proteins that have been implicated in modulating various biological processes. The presence of inherent polyploidy and genome complexity has limited the identification and characterization of 14-3-3 proteins from globally important Brassica crops. Through data mining of Brassica rapa, the model Brassica genome, we identified 21 members encoding 14-3-3 proteins namely, BraA.GRF14.a to BraA.GRF14.u. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that B. rapa contains both ε (epsilon) and non-ε 14-3-3 isoforms, having distinct intron-exon structural organization patterns. The non-ε isoforms showed lower divergence rate (Ks < 0.45) compared to ε protein isoforms (Ks > 0.48), suggesting class-specific divergence pattern. Synteny analysis revealed that mesohexaploid B. rapa genome has retained 1-5 orthologs of each Arabidopsis 14-3-3 gene, interspersed across its three fragmented sub-genomes. qRT-PCR analysis showed that 14 of the 21 BraA.GRF14 were expressed, wherein a higher abundance of non-ε transcripts was observed compared to the ε genes, indicating class-specific transcriptional bias. The BraA.GRF14 genes showed distinct expression pattern during plant developmental stages and in response to abiotic stress, phytohormone treatments, and nutrient deprivation conditions. Together, the distinct expression pattern and differential regulation of BraA.GRF14 genes indicated the occurrence of functional divergence of B. rapa 14-3-3 proteins during plant development and stress responses.
Keywords: 14-3-3; Brassica rapa; expression differentiation; gene divergence; polyploidy.
Figures


References
-
- Bachmann M., Huber J. L., Athwal G. S., Wu K., Ferl R. J., Huber S. C. (1996). 14-3-3 proteins associate with the regulatory phosphorylation site of spinach leaf nitrate reductase in an isoform-specific manner and reduce dephosphorylation of Ser-543 by endogenous protein phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 398, 26–30. 10.1016/s0014-5793(96)01188-x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

