Recruiting a U.S. national sample of HIV-negative gay and bisexual men to complete at-home self-administered HIV/STI testing and surveys: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 26858776
- PMCID: PMC4743043
- DOI: 10.1007/s13178-015-0212-y
Recruiting a U.S. national sample of HIV-negative gay and bisexual men to complete at-home self-administered HIV/STI testing and surveys: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
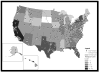
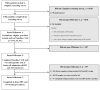
We describe enrollment for the One Thousand Strong panel, present characteristics of the panel relative to other large U.S. national studies of gay and bisexual men (GBM), and examine demographic and behavioral characteristics that were associated with passing enrollment milestones. A U.S. national sample of HIV-negative men were enrolled via an established online panel of over 22,000 GBM. Participants (n = 1071) passed three milestones to join our panel. Milestone 1 was screening eligible and providing informed consent. Milestone 2 involved completing an hour-long at-home computer-assisted self-interview (CASI) survey. Milestone 3 involved completing at-home self-administered rapid HIV testing and collecting/returning urine and rectal samples for gonorrhea and chlamydia testing. Compared to those who completed milestones: those not passing milestone 1 were more likely to be non-White and older; those not passing milestone 2 were less likely to have insurance or a primary care physician; and those not passing milestone 3 were less educated, more likely to be bisexual as opposed to gay, more likely to live in the Midwest, had fewer male partners in the past year, and less likely to have tested for HIV in the past year. Effect sizes for significant findings were small. We successfully enrolled a national sample of HIV-negative GBM who completed at-home CASI assessments and at-home self-administered HIV and urine and rectal STI testing. This indicates high feasibility and acceptability of incorporating self-administered biological assays into otherwise fully online studies. Differences in completion of study milestones indicate a need for further investigation into the reasons for lower engagement by certain groups.
Keywords: HIV; Internet; STI testing; bars/clubs; condomless anal sex; gay and bisexual men; men who have sex with men; recruitment; sex parties; venues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Adam BD, Murray J, Ross S, Oliver J, Lincoln SG, Rynard V. HIVstigma.com, an innovative web-supported stigma reduction intervention for gay and bisexual men. Health Education Research. 2011;26(5):795–807. doi: 10.1093/her/cyq078. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bell D, Valentine G. Queer country: rural lesbian and gay lives. Journal of Rural Studies. 1995;11(2):113–122.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous