Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Resolving Within 48 Hours in a Normotensive Patient Who Underwent Thoracic Spine Surgery
- PMID: 26858804
- PMCID: PMC4737042
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr2472w
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Resolving Within 48 Hours in a Normotensive Patient Who Underwent Thoracic Spine Surgery
Abstract
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) usually manifests with severe headaches, seizures, and visual disturbances due to uncontrollable hypertension. A patient (age in the early 60s) with a history of renal cell cancer presented with lower-extremity weakness and paresthesias. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the thoracic spine revealed a T8 vertebral body metastatic lesion with cord compression at that level. The patient underwent preoperative embolization of the tumor followed by posterior resection and placement of percutaneous pedicle screws and rods. Postoperatively, the patient experienced decreased visual acuity bilaterally. Abnormal MRI findings consisted of T2 hyperintense lesions and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery changes in both occipital lobes, consistent with the unique brain imaging pattern associated with PRES. The patient's blood pressure was normal and stable from the first day of hospitalization. The patient was kept on high-dose steroid therapy, which was started intraoperatively, and improved within 48 hours after symptom onset.
Keywords: Cortical blindness; Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; Prone surgery.
Figures
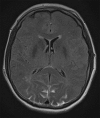
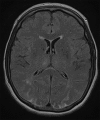
Similar articles
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome following elevated mean arterial pressures for cervical spinal cord injury.J Spinal Cord Med. 2018 Jan;41(1):111-114. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2016.1250030. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Spinal Cord Med. 2018. PMID: 27917700 Free PMC article.
-
[Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003 Nov-Dec;131(11-12):461-6. doi: 10.2298/sarh0312461p. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003. PMID: 15114789 Serbian.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome following a thoracic discectomy-induced dural leak: case report.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Nov;25(5):586-590. doi: 10.3171/2016.4.SPINE1623. Epub 2016 Jun 3. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 27258477
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) induced by pazopanib, a multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in a patient with soft-tissue sarcoma: case report and review of the literature.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Apr;36(2):346-349. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0521-5. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29067537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variant Type of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Associated with Deep Brain Hemorrhage: Case Report and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2020 Feb;134:176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.196. Epub 2019 Nov 8. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31712110 Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical Blindness after Cervical Spine Surgery in Supine Position - A Rare Case Report and Review of the Literature.Asian J Neurosurg. 2021 May 28;16(2):406-411. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_473_20. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Asian J Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34268176 Free PMC article.
-
Can Post-Operative Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) Be Considered an Insidious Rare Surgical Complication?Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 23;13(5):706. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050706. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome following spine surgery: A case report and review of the literature.Radiol Case Rep. 2022 Dec 1;18(2):635-638. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.11.004. eCollection 2023 Feb. Radiol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36471737 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in the setting of trauma: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;72:528-532. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.06.061. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32698281 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome following cervical spine surgery: insights from an interesting case.Childs Nerv Syst. 2023 Apr;39(4):1089-1092. doi: 10.1007/s00381-022-05726-x. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Childs Nerv Syst. 2023. PMID: 36571596
References
-
- Stambough JL, Dolan D, Werner R, Godfrey E. Ophthalmologic complications associated with prone positioning in spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15(3):156–165. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
