Disinfectant-susceptibility of multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated in Japan
- PMID: 26858829
- PMCID: PMC4745152
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-016-0102-y
Disinfectant-susceptibility of multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated in Japan
Abstract
Background: Multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been an important problem in public health around the world. However, limited information about disinfectant-susceptibility of multi-drug-resistant strain of M. tuberculosis was available.
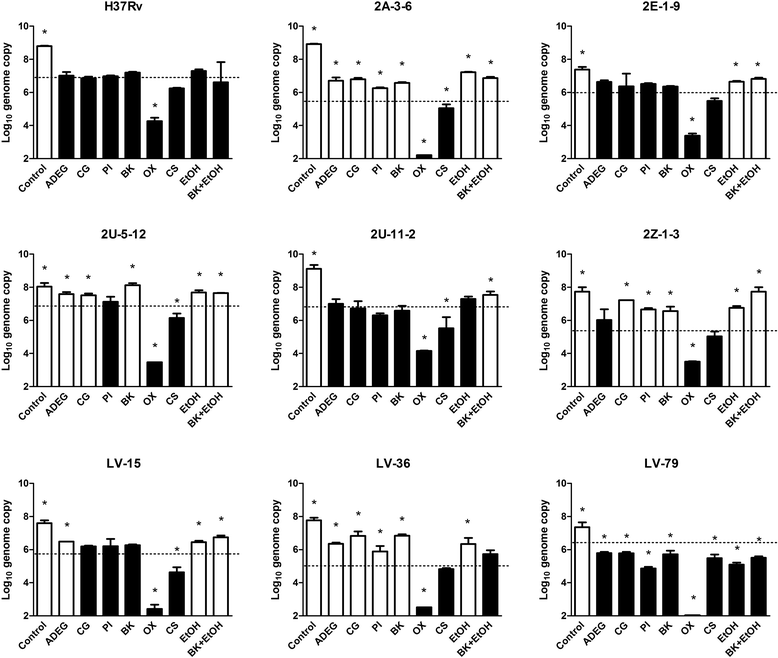
Findings: We studied susceptibility of several Japanese isolates of multi-drug-resistant M. tuberculosis against disinfectants, which are commonly used in clinical and research laboratories. We selected a laboratory reference strain (H37Rv) and eight Japanese isolates, containing five drug-susceptible strains and three multi-drug-resistant strains, and determined profiles of susceptibility against eight disinfectants. The M. tuberculosis strains were distinguished into two groups by the susceptibility profile. There was no relationship between multi-drug-resistance and disinfectant-susceptibility in the M. tuberculosis strains. Cresol soap and oxydol were effective against all strains we tested, regardless of drug resistance.
Conclusions: Disinfectant-resistance is independent from multi-drug-resistance in M. tuberculosis. Cresol soap and oxydol were effective against all strains we tested, regardless of drug resistance.
Keywords: Disinfectant; Microbicide; Multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Frontier of mycobacterium research--host vs. mycobacterium].Kekkaku. 2005 Sep;80(9):613-29. Kekkaku. 2005. PMID: 16245793 Japanese.
-
[Sensitivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to levofloxacin].Antibiot Khimioter. 2002;47(6):28-30. Antibiot Khimioter. 2002. PMID: 12422645 Russian.
-
Drug susceptibility profiles of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates at Jaipur.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002 Apr-Jun;20(2):76-8. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 17657036
-
[Drug-resistant tuberculosis: resistance mechanisms and drug susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis].Acta Med Croatica. 2004;58(4):323-8. Acta Med Croatica. 2004. PMID: 15700689 Review. Croatian.
-
[Extensively drug resistant and extremely drug resistant tuberculosis forms after multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: new faces of the old disease].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011 Jan;45(1):181-95. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011. PMID: 21341173 Review. Turkish.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium vaccae Adaptation to Disinfectants and Hand Sanitisers, and Evaluation of Cross-Tolerance with Antimicrobials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 27;9(9):544. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090544. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32867093 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the risk of resistance to cationic biocides incorporating realism-based and biophysical approaches.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 20;49(1):kuab074. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab074. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34718634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

