Quantification of cortisol in human eccrine sweat by liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 26858998
- PMCID: PMC5376102
- DOI: 10.1039/c5an02387d
Quantification of cortisol in human eccrine sweat by liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
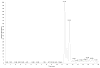
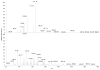
Cortisol has long been recognized as the "stress biomarker" in evaluating stress related disorders. Plasma, urine or saliva are the current source for cortisol analysis. The sampling of these biofluids is either invasive or has reliability problems that could lead to inaccurate results. Sweat has drawn increasing attention as a promising source for non-invasive stress analysis. A sensitive HPLC-MS/MS method was developed for the quantitation of cortisol ((11β)-11,17,21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione) in human eccrine sweat. At least one unknown isomer that has previously not been reported and could potentially interfere with quantification was separated from cortisol with mixed mode RP HPLC. Detection of cortisol was carried out using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) and selected reaction monitoring (SRM) in positive ion mode, using cortisol-9,11,12,12-D4 as internal standard. LOD and LOQ were estimated to be 0.04 ng ml(-1) and 0.1 ng ml(-1), respectively. Linear range of 0.10-25.00 ng ml(-1) was obtained. Intraday precision (2.5%-9.7%) and accuracy (0.5%-2.1%), interday precision (12.3%-18.7%) and accuracy (7.1%-15.1%) were achieved. This method has been successfully applied to the cortisol analysis of human eccrine sweat samples. This is the first demonstration that HPLC-MS/MS can be used for the sensitive and highly specific determination of cortisol in human eccrine sweat in the presence of at least one isomer that has similar hydrophobicity as cortisol. This study demonstrated that human eccrine sweat could be used as a promising source for non-invasive assessment of stress biomarkers such as cortisol and other steroid hormones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fast accurate quantification of salivary cortisol and cortisone in a large-scale clinical stress study by micro-UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS using a surrogate calibrant approach.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Oct 1;1182:122939. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122939. Epub 2021 Sep 11. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34547590
-
Simultaneous measurements of cortisol and cortisone in urine and hair for the assessment of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity among methadone maintenance treatment patients with LC-ESI-MS/MS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Oct 15;969:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Aug 10. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25151333
-
Quantitative analysis of hydrocortisone in human urine using a high-performance liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric-atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization method.J Chromatogr Sci. 2001 Feb;39(2):59-64. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/39.2.59. J Chromatogr Sci. 2001. PMID: 11245227
-
Cortisol Immunosensors: A Literature Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;13(2):285. doi: 10.3390/bios13020285. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Analysis of Cortisol and Its Derivatives.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1140:649-664. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-15950-4_39. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31347077 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of cortisol dynamics in human sweat using a graphene-based wireless mHealth system.Matter. 2020 Apr 1;2(4):921-937. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2020.01.021. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Matter. 2020. PMID: 32266329 Free PMC article.
-
Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Jun 10;11(6):191. doi: 10.3390/bios11060191. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200643 Free PMC article.
-
Sweat and saliva cortisol response to stress and nutrition factors.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 4;10(1):19050. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75871-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33149196 Free PMC article.
-
Working Up a Good Sweat - The Challenges of Standardising Sweat Collection for Metabolomics Analysis.Clin Biochem Rev. 2017 Feb;38(1):13-34. Clin Biochem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28798503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
StressFit: a hybrid wearable physicochemical sensor suite for simultaneously measuring electromyogram and sweat cortisol.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 29;14(1):29667. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81042-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39613840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Judd LL, Schettler PJ, Brown ES, Wolkowitz OM, Sternberg EM, Bender BG, et al. Adverse consequences of glucocortoid medication: psychological, cognitive and behavioral effects. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- Baid SK, Sinaii N, Wade M, Rubino D, Nieman LK. Radioimmunoassay and tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bedtime salivary cortisol levels: a comparison of assays to establish hypercortisolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8):3102–7. - PubMed
-
- Hansen AM, Garde AH, Christensen JM, Eller NH, Netterstrøm B. Evaluation of a radioimmunoassay and establishment of a reference interval for salivary cortisol in healthy subjects in Denmark. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2003;63(4):303–10. - PubMed
-
- Hayes LD, Sculthorpe N, Young JD, Baker JS, Grace FM. Critical difference applied to exercise-induced salivary testosterone and cortisol using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): distinguishing biological from statistical change. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(4):991–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical