Serine/Threonine Kinase MLK4 Determines Mesenchymal Identity in Glioma Stem Cells in an NF-κB-dependent Manner
- PMID: 26859459
- PMCID: PMC4837946
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.01.005
Serine/Threonine Kinase MLK4 Determines Mesenchymal Identity in Glioma Stem Cells in an NF-κB-dependent Manner
Abstract
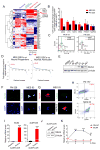
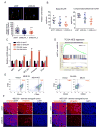
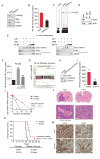
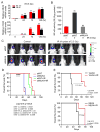
Activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) induces mesenchymal (MES) transdifferentiation and radioresistance in glioma stem cells (GSCs), but molecular mechanisms for NF-κB activation in GSCs are currently unknown. Here, we report that mixed lineage kinase 4 (MLK4) is overexpressed in MES but not proneural (PN) GSCs. Silencing MLK4 suppresses self-renewal, motility, tumorigenesis, and radioresistance of MES GSCs via a loss of the MES signature. MLK4 binds and phosphorylates the NF-κB regulator IKKα, leading to activation of NF-κB signaling in GSCs. MLK4 expression is inversely correlated with patient prognosis in MES, but not PN high-grade gliomas. Collectively, our results uncover MLK4 as an upstream regulator of NF-κB signaling and a potential molecular target for the MES subtype of glioblastomas.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; glioblastoma; proneural-mesenchymal transition.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444:756–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS083767/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH/NINDSR01 NS083767/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH/NINDS 1R01NS0 75291-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS093843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS095634/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA175875/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA201402/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS095634/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2P50CA1270011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA183991/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH/NCI P01 CA163205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA159811/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS093843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087913/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA163205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM089571/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH R01CA158911/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

