Invasive mouse gastric adenocarcinomas arising from Lgr5+ stem cells are dependent on crosstalk between the Hedgehog/GLI2 and mTOR pathways
- PMID: 26859571
- PMCID: PMC4891118
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7182
Invasive mouse gastric adenocarcinomas arising from Lgr5+ stem cells are dependent on crosstalk between the Hedgehog/GLI2 and mTOR pathways
Abstract
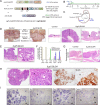
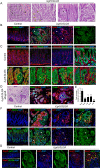
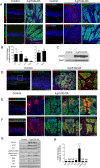
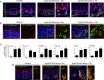
Gastric adenocarcinoma is the third most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Here we report a novel, highly-penetrant mouse model of invasive gastric cancer arising from deregulated Hedgehog/Gli2 signaling targeted to Lgr5-expressing stem cells in adult stomach. Tumor development progressed rapidly: three weeks after inducing the Hh pathway oncogene GLI2A, 65% of mice harbored in situ gastric cancer, and an additional 23% of mice had locally invasive tumors. Advanced mouse gastric tumors had multiple features in common with human gastric adenocarcinomas, including characteristic histological changes, expression of RNA and protein markers, and the presence of major inflammatory and stromal cell populations. A subset of tumor cells underwent epithelial-mesenchymal transition, likely mediated by focal activation of canonical Wnt signaling and Snail1 induction. Strikingly, mTOR pathway activation, based on pS6 expression, was robustly activated in mouse gastric adenocarcinomas from the earliest stages of tumor development, and treatment with rapamycin impaired tumor growth. GLI2A-expressing epithelial cells were detected transiently in intestine, which also contains Lgr5+ stem cells, but they did not give rise to epithelial tumors in this organ. These findings establish that deregulated activation of Hedgehog/Gli2 signaling in Lgr5-expressing stem cells is sufficient to drive gastric adenocarcinoma development in mice, identify a critical requirement for mTOR signaling in the pathogenesis of these tumors, and underscore the importance of tissue context in defining stem cell responsiveness to oncogenic stimuli.
Keywords: GLI2; Lgr5; gastric cancer; mTOR; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
AAD served as member of a scientific advisory board for Novartis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gastric cancer (GC) patients with hedgehog pathway activation: PTCH1 and GLI2 as independent prognostic factors.Target Oncol. 2013 Dec;8(4):271-80. doi: 10.1007/s11523-013-0253-1. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Target Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23371028
-
Autophagy is related to the hedgehog signaling pathway in human gastric adenocarcinoma: prognostic significance of Beclin-1 and Gli2 expression in human gastric adenocarcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2015 Apr;211(4):308-15. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 25512258
-
NANOGP8 is the key regulator of stemness, EMT, Wnt pathway, chemoresistance, and other malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cells.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 24;13(4):e0192436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192436. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29689047 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric epithelial stem cells.Gastroenterology. 2011 Feb;140(2):412-24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21144849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric cancer stem cells: therapeutic targets.Gastric Cancer. 2014 Jan;17(1):13-25. doi: 10.1007/s10120-013-0254-x. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Gastric Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23563919 Review.
Cited by
-
Initiation and Maintenance of Gastric Cancer: A Focus on CD44 Variant Isoforms and Cancer Stem Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Mar 14;4(1):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.03.003. eCollection 2017 Jul. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28560289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Aggressive Gastric Cancer Phenotypes via Heat Shock Factor 1-Mediated Secretion of Extracellular Vesicles.Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 1;81(7):1639-1653. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2756. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33547159 Free PMC article.
-
Phase 1 trial of Vismodegib and Erlotinib combination in metastatic pancreatic cancer.Pancreatology. 2020 Jan;20(1):101-109. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2019.11.011. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Pancreatology. 2020. PMID: 31787526 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gli2 mediates the development of castration‑resistant prostate cancer.Int J Oncol. 2020 Jul;57(1):100-112. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5044. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32319599 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Hedgehog/GLI Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 15;11(4):538. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040538. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30991683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Ester S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. 2013. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer;
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Wang K, Yuen ST, Xu J, Lee SP, Yan HH, Shi ST, Siu HC, Deng S, Chu KM, Law S, Chan KH, Chan AS, Tsui WY, et al. Whole-genome sequencing and comprehensive molecular profiling identify new driver mutations in gastric cancer. Nat Genet. 2014;46:573–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

