Aortic VCAM-1: an early marker of vascular inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 26859834
- PMCID: PMC4831368
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12790
Aortic VCAM-1: an early marker of vascular inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
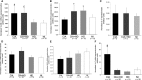
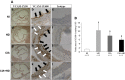
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). There are limited experimental data on vascular involvement in arthritis models. To study the link between CVD and inflammation in RA, we developed a model of vascular dysfunction and articular inflammation by collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in C57Bl/6 (B6) mice. We studied the expression of vascular inflammatory markers in CIA with and without concomitant hyperlipidic diet (HD). Collagen-induced arthritis was induced with intradermal injection of chicken type-II collagen followed by a boost 21 days later. Mice with and without CIA were fed a standard diet or an HD for 12 weeks starting from the day of the boost. Arthritis severity was evaluated with a validated clinical score. Aortic mRNA levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and interleukin-17 were analysed by quantitative RT-PCR. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 localization in the aortic sinus was determined by immunohistochemistry. Atherosclerotic plaque presence was assessed in aortas. Collagen-induced arthritis was associated with increased expression of VCAM-1, independent of diet. VCAM-1 overexpression was detectable as early as 4 weeks after collagen immunization and persisted after 15 weeks. The HD induced atheroma plaque formation and aortic iNOS expression regardless of CIA. Concomitant CIA and HD had no additive effect on atheroma or VCAM-1 or iNOS expression. CIA and an HD diet induced a distinct and independent expression of large-vessel inflammation markers in B6 mice. This model may be relevant for the study of CVD in RA.
Keywords: arthritis rheumatoid; atherosclerosis; collagen-induced arthritis; hyperlipidic diet; inflammation; mice; vasculature.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) blockade in collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint involvement and alters B cell trafficking.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Apr;128(1):44-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01794.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11982589 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen-induced arthritis increases inducible nitric oxide synthase not only in aorta but also in the cardiac and renal microcirculation of mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Mar;183(3):341-9. doi: 10.1111/cei.12728. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26456019 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2 Receptor Is Involved in Alleviation of Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:496759. doi: 10.1155/2015/496759. Epub 2015 Nov 29. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26693483 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Value of Murine Delayed-type Hypersensitivity Arthritis: A Robust Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis in C57BL/6 Mice.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Feb;120(2):108-114. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12657. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27553641 Review.
-
Experimental animal models for rheumatoid arthritis.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018 Jun;40(3):193-200. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2018.1434793. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018. PMID: 29433367 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytochrome P450: Polymorphisms and Roles in Cancer, Diabetes and Atherosclerosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Aug 24;19(8):2057-2070. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2057. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30139042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular and lipid-lowering effects of a marine lipoprotein extract in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jan 22;20(3):292-306. doi: 10.7150/ijms.80727. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36860672 Free PMC article.
-
Induced, but not natural, regulatory T cells retain phenotype and function following exposure to inflamed synovial fibroblasts.Sci Adv. 2020 Oct 28;6(44):eabb0606. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb0606. Print 2020 Oct. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33115734 Free PMC article.
-
The VEGFA156b isoform is dysregulated in senescent endothelial cells and may be associated with prevalent and incident coronary heart disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Feb 2;132(3):313-325. doi: 10.1042/CS20171556. Print 2018 Feb 14. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29330351 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecules- (un)Attainable Targets for Nanomedicines.Front Med Technol. 2022 Apr 7;4:846065. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.846065. eCollection 2022. Front Med Technol. 2022. PMID: 35463298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosales Alexander JL, Cantero‐Hinojosa J, Salvatierra J, et al Cardiovascular risk assessment according to a national calibrated score risk index in psoriatic arthritis patients without clinically evident cardiovascular disease or classic atherosclerosis risk factors. Joint Bone Spine. 2014; 81: 164–8. - PubMed
-
- Soubrier M, Chamoux NB, Tatar Z, et al Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2014; 81: 298–302. - PubMed
-
- Peters MJL, van Halm VP, Voskuyl AE, et al Does rheumatoid arthritis equal diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A prospective study Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 61: 1571–9. - PubMed
-
- Holmqvist ME, Wedren S, Jacobsson LT, et al Rapid increase in myocardial infarction risk following diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis amongst patients diagnosed between 1995 and 2006. J Intern Med. 2010; 268: 578–85. - PubMed
-
- Del Rincon ID, Williams K, Stern MP, et al High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44: 2737–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

