An intra-cerebral abscess in a patient with Eisenmenger syndrome: An unusual case
- PMID: 26859871
- PMCID: PMC4818319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.01.025
An intra-cerebral abscess in a patient with Eisenmenger syndrome: An unusual case
Abstract
Introduction: We present an unusual case where a large intra-cerebral abscess with severe complications was treated successfully with medical management alone in a patient with Eisenmenger syndrome.
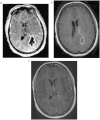
Presentation of case: A 40 year old patient with Eisenmenger syndrome presented with a seven day history of headache, neck pain and intermittent vomiting and fever. The only neurological examination finding was blurred vision. MRI revealed a large left occipital lobe abscess, which subsequently ruptured into the lateral ventricle with associated ventriculitis and hydrocephalus. This complicated abscess was successfully treated with intravenous antibiotics alone, with complete resolution of the abscess and hydrocephalus on MRI at 13 months post-diagnosis.
Discussion: Patients with congenital cyanotic heart conditions, like Eisenmenger syndrome, are at increased risk of developing intra-cerebral abscesses. Effectively managing large abscesses with associated intra-ventricular rupture and hydrocephalus in these patients without any form of surgical intervention, including aspiration, is extremely rare.
Conclusion: Patients with congenital cyanotic heart disease who develop large intra-cerebral abscesses with severe complications, which would normally warrant surgical intervention, have the potential to be successfully treated with antibiotics alone with excellent outcome.
Keywords: Eisenmenger syndrome; Intracerebral abscess.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral abscess as a neurosurgical emergency in Eisenmenger syndrome: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022 Aug 1;4(5):CASE2252. doi: 10.3171/CASE2252. Print 2022 Aug 1. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022. PMID: 36088558 Free PMC article.
-
Brain abscess associated with ventricular septal defect and Eisenmenger syndrome: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr;81:105799. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.105799. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33756163 Free PMC article.
-
Current treatment of brain abscess in patients with congenital cyanotic heart disease.Neurosurgery. 1997 Dec;41(6):1270-8; discussion 1278-9. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199712000-00006. Neurosurgery. 1997. PMID: 9402578
-
Eisenmenger syndrome--a unique form of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2009;110(12):757-64. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2009. PMID: 20196469 Review.
-
[A case of amebic brain abscess].No Shinkei Geka. 2007 Sep;35(9):919-25. No Shinkei Geka. 2007. PMID: 17867313 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Giant Actinomyces brain abscess in an immunocompetent child: A management strategy.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Jul 6;12:325. doi: 10.25259/SNI_164_2021. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34345466 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral abscess as a neurosurgical emergency in Eisenmenger syndrome: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022 Aug 1;4(5):CASE2252. doi: 10.3171/CASE2252. Print 2022 Aug 1. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2022. PMID: 36088558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathisen G.E., Johnson J.P. Brain abscess. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997;25(4):763–779. - PubMed
-
- Takeshita M., Kagawa M., Yato S., Izawa M., Onda H., Takakura A. Current treatment of brain abscess in patients with congenital cyanotic heart disease. Neurosurgery. 1997;41:1270–1279. - PubMed
-
- Takeshita M., Kawamata T., Izawa M., Hori T. Prodromal signs and clinical factors influencing outcome in patients with intraventricular rupture of purulent brain abscess. Neurosurgery. 2001;48(2):310–316. - PubMed
-
- Moorthy R.K., Rajshekhar V. Management of brain abscess: an overview. Neurosurg. Focus. 2008;24 E3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

