Optical imaging of pre-invasive breast cancer with a combination of VHHs targeting CAIX and HER2 increases contrast and facilitates tumour characterization
- PMID: 26860296
- PMCID: PMC4747965
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-016-0166-y
Optical imaging of pre-invasive breast cancer with a combination of VHHs targeting CAIX and HER2 increases contrast and facilitates tumour characterization
Abstract
Background: Optical molecular imaging is an emerging novel technology with applications in the diagnosis of cancer and assistance in image-guided surgery. A high tumour-to-background (T/B) ratio is crucial for successful imaging, which strongly depends on tumour-specific probes that rapidly accumulate in the tumour, while non-bound probes are rapidly cleared. Here, using pre-invasive breast cancer as a model, we investigate whether the use of combinations of probes with different target specificities results in higher T/B ratios and whether dual-spectral imaging leads to improvements in tumour characterization.
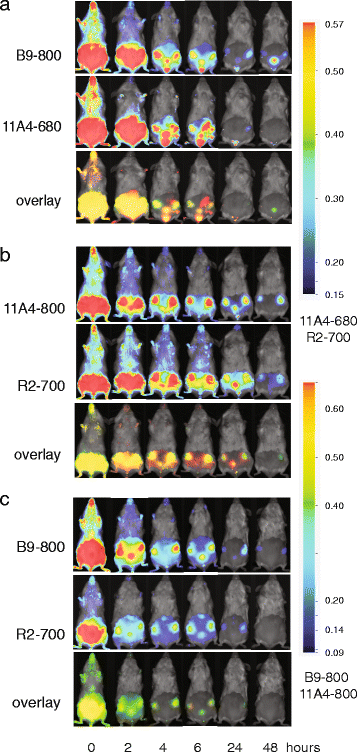
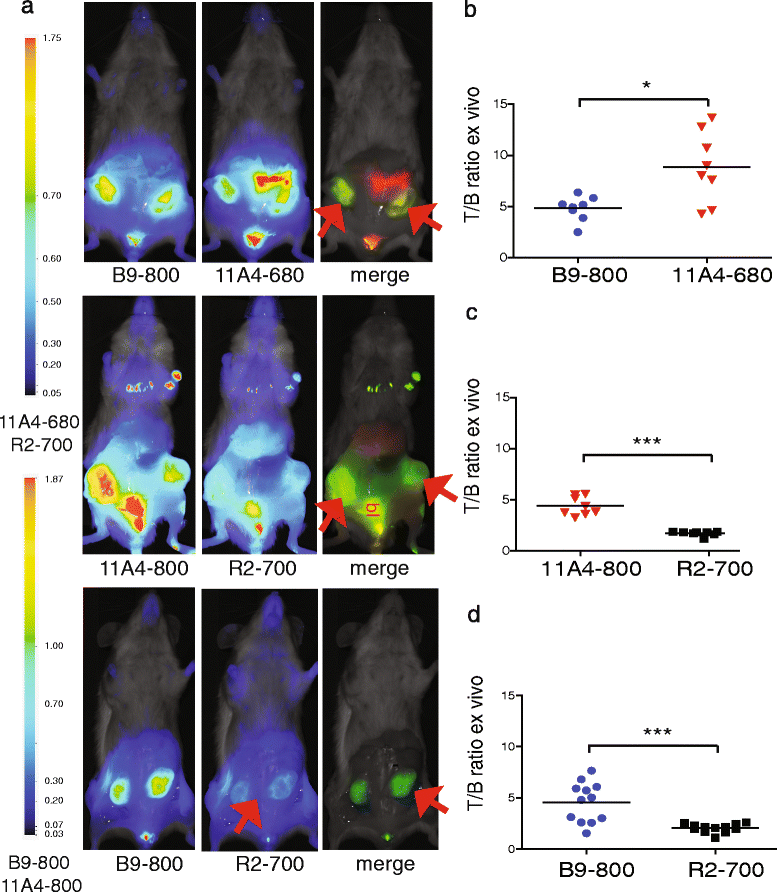
Methods: We performed optical molecular imaging of an orthotopic breast cancer model mimicking ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). A combination of carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX)- and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-specific variable domains of the heavy chain from heavy-chain antibodies (VHHs) was conjugated either to the same fluorophore (IRDye800CW) to evaluate T/B ratios or to different fluorophores (IRDye800CW, IRDye680RD or IRDye700DX) to analyse the expression of CAIX and HER2 simultaneously through dual-fluorescence detection. These experiments were performed non-invasively in vivo, in a mimicked intra-operative setting, and ex vivo on tumour sections.
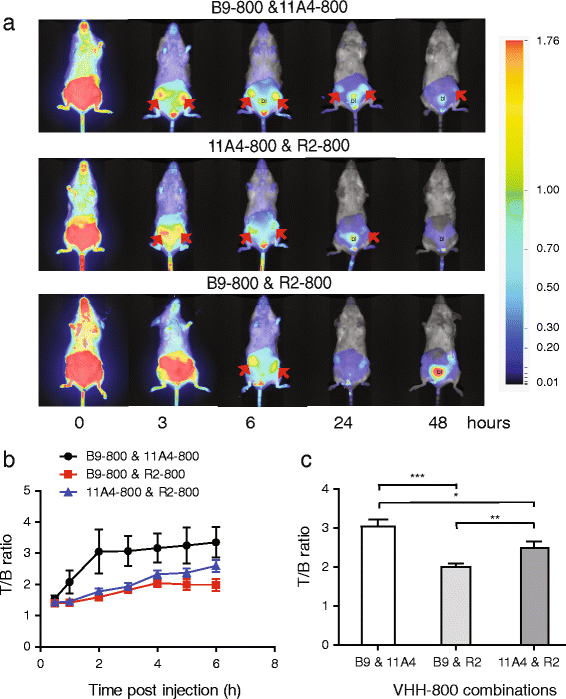
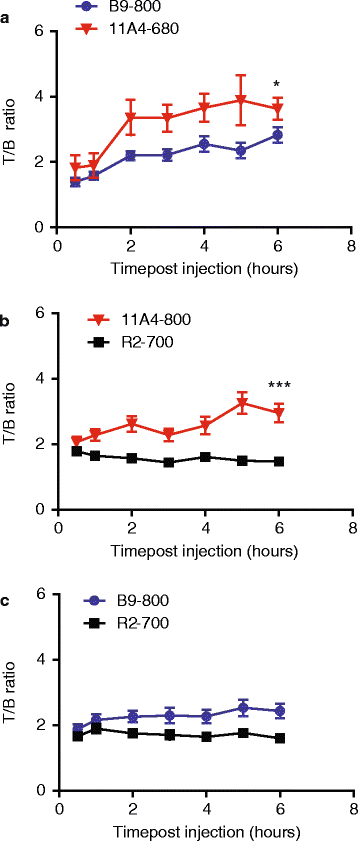
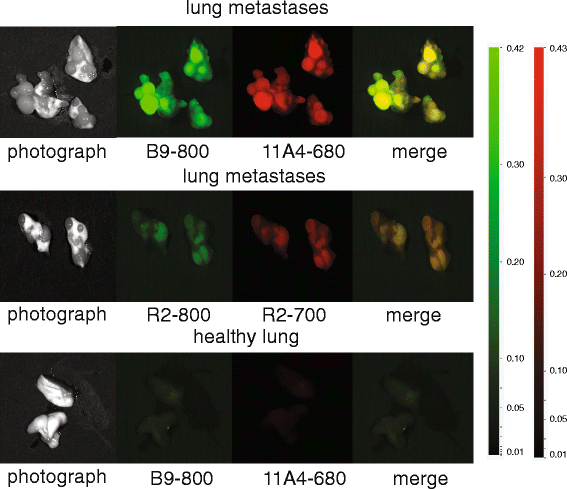
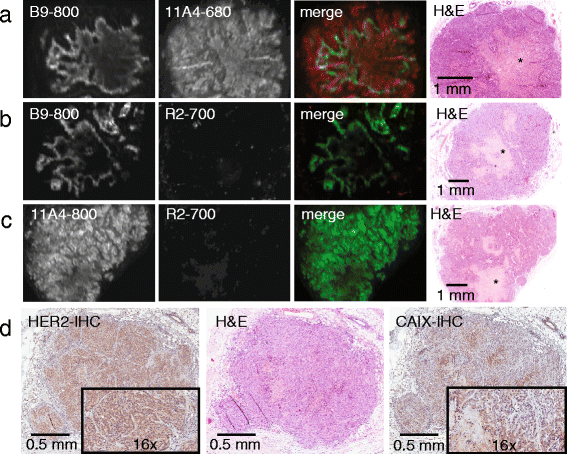
Results: Application of the CAIX- and HER2-specific VHH combination resulted in an increase of the T/B ratio, as compared to T/B ratios obtained from each of these single VHHs together with an irrelevant VHH. This dual tumour marker-specific VHH combination also enabled the detection of small metastases in the lung. Furthermore, dual-spectral imaging enabled the assessment of the expression status of both CAIX and HER2 in a mimicked intra-operative setting, as well as on tumour sections, which was confirmed by immunohistochemistry.
Conclusions: These results establish the feasibility of the use of VHH 'cocktails' to increase T/B ratios and improve early detection of heterogeneous tumours and the use of multispectral molecular imaging to facilitate the assessment of the target expression status of tumours and metastases, both invasive or non-invasively.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CAIX; Fluorescence pathology; HER2; Nanobody or VHH; Optical molecular imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-Targeting Fluorescent Nanobodies for Optical Molecular Imaging of Pre-Invasive Breast Cancer.Mol Imaging Biol. 2016 Aug;18(4):535-44. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0909-6. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016. PMID: 26589824 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid optical imaging of human breast tumour xenografts using anti-HER2 VHHs site-directly conjugated to IRDye 800CW for image-guided surgery.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013 Oct;40(11):1718-29. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2471-2. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23778558
-
Molecular imaging with a fluorescent antibody targeting carbonic anhydrase IX can successfully detect hypoxic ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jul;140(2):263-72. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2635-6. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23860929
-
Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CAIX), Cancer, and Radiation Responsiveness.Metabolites. 2018 Feb 10;8(1):13. doi: 10.3390/metabo8010013. Metabolites. 2018. PMID: 29439394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How and Why Are Cancers Acidic? Carbonic Anhydrase IX and the Homeostatic Control of Tumour Extracellular pH.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 18;12(6):1616. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061616. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32570870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single domain Camelid antibody fragments for molecular imaging and therapy of cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 8;13:1257175. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1257175. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37746282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobody-Based Delivery Systems for Diagnosis and Targeted Tumor Therapy.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 2;8:1442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01442. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29163515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-Specific Dual-Labeling of a VHH with a Chelator and a Photosensitizer for Nuclear Imaging and Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of EGFR-Positive Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 23;13(3):428. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030428. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498707 Free PMC article.
-
NANOBODIES®: A Review of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):5994. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065994. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36983063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Wavelength Fluorescence in Image-Guided Surgery, Clinical Feasibility and Future Perspectives.Mol Imaging. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1536012120962333. doi: 10.1177/1536012120962333. Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33125289 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinheiro C, Sousa B, Albergaria A, Paredes J, Dufloth R, Vieira D, et al. GLUT1 and CAIX expression profiles in breast cancer correlate with adverse prognostic factors and MCT1 overexpression. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26:1279–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

