Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of AKI
- PMID: 26860342
- PMCID: PMC4849836
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015070740
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of AKI
Abstract
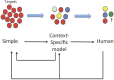
In this article, we review the current evidence for the cellular and molecular mechanisms of AKI, focusing on epithelial cell pathobiology and related cell-cell interactions, using ischemic AKI as a model. Highlighted are the clinical relevance of cellular and molecular targets that have been investigated in experimental models of ischemic AKI and how such models might be improved to optimize translation into successful clinical trials. In particular, development of more context-specific animal models with greater relevance to human AKI is urgently needed. Comorbidities that could alter patient susceptibility to AKI, such as underlying diabetes, aging, obesity, cancer, and CKD, should also be considered in developing these models. Finally, harmonization between academia and industry for more clinically relevant preclinical testing of potential therapeutic targets and better translational clinical trial design is also needed to achieve the goal of developing effective interventions for AKI.
Keywords: acute renal failure; kidney; pathophysiology of renal disease and progression.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Zager RA: Plasma membrane cholesterol: a critical determinant of cellular energetics and tubular resistance to attack. Kidney Int 58: 193–205, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Lorz C, Ortiz A, Justo P, González-Cuadrado S, Duque N, Gómez-Guerrero C, Egido J: Proapoptotic Fas ligand is expressed by normal kidney tubular epithelium and injured glomeruli. J Am Soc Nephrol 11: 1266–1277, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Mahmoudi M, Willgoss D, Cuttle L, Yang T, Pat B, Winterford C, Endre Z, Johnson DW, Gobé GC: In vivo and in vitro models demonstrate a role for caveolin-1 in the pathogenesis of ischaemic acute renal failure. J Pathol 200: 396–405, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Fujigaki Y, Sakakima M, Sun Y, Goto T, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Tsuji T, Yamamoto T, Hishida A: Immunohistochemical study on caveolin-1alpha in regenerating process of tubular cells in gentamicin-induced acute tubular injury in rats. Virchows Arch 450: 671–681, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

