Identification and functional analysis of a bacteriocin, pyocin S6, with ribonuclease activity from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis clinical isolate
- PMID: 26860427
- PMCID: PMC4905994
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.339
Identification and functional analysis of a bacteriocin, pyocin S6, with ribonuclease activity from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis clinical isolate
Abstract
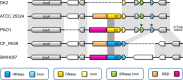
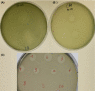
S-type pyocins are bacteriocins produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates to antagonize or kill other strains of the same species. They have a modular organization comprising a receptor-binding domain recognizing a surface constituent of the target bacterium, a domain for translocation through the periplasm, and a killing or toxic domain with DNase, tRNase, or pore-forming activity. Pyocins S2, S3, S4, and S5 recognize TonB-dependent ferri-siderophore receptors in the outer membrane. We here describe a new nuclease bacteriocin, pyocin S6, encoded in the genome of a P. aeruginosa cystic fibrosis (CF) clinical isolate, CF_PA39. Similarly to pyocins S1 and S2, the S6 toxin-immunity gene tandem was recruited to the genomic region encoding exotoxin A. The pyocin S6 receptor-binding and translocation domains are identical to those of pyocin S1, whereas the killing domain is similar to the 16S ribonuclease domain of Escherichia coli colicin E3. The cytotoxic activity was abolished in pyocin S6 forms with a mutation in the colicin E3-equivalent catalytic motif. The CF_PA39 S6 immunity gene displays a higher expression level than the gene encoding the killing protein, the latter being only detected when bacteria are grown under iron-limiting conditions. In the S1-pyocinogenic strain P. aeruginosa ATCC 25324 and pyocin S2 producer P. aeruginosa PAO1, a remnant of the pyocin S6 killing domain and an intact S6-type immunity gene are located downstream of their respective pyocin operons. Strain PAO1 is insensitive for pyocin S6, and its S6-type immunity gene provides protection against pyocin S6 activity. Purified pyocin S6 inhibits one-fifth of 110 P. aeruginosa CF clinical isolates tested, showing clearer inhibition zones when the target cells are grown under iron limitation. In this panel, about half of the CF clinical isolates were found to host the S6 genes. The pyocin S6 locus is also present in the genome of some non-CF clinical isolates.
Keywords: 16S ribonuclease; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; cystic fibrosis; iron; pyocins..
© 2016 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Colicin M-Type Bacteriocin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Targeting the HxuC Heme Receptor Requires a Novel Immunity Partner.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Aug 31;84(18):e00716-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00716-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29980560 Free PMC article.
-
Pore-forming pyocin S5 utilizes the FptA ferripyochelin receptor to kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiology (Reading). 2014 Feb;160(Pt 2):261-269. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.070672-0. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Microbiology (Reading). 2014. PMID: 24217175
-
Heterogenous Susceptibility to R-Pyocins in Populations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sourced from Cystic Fibrosis Lungs.mBio. 2021 May 4;12(3):e00458-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00458-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33947755 Free PMC article.
-
The pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biochimie. 2002 May-Jun;84(5-6):499-510. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01422-0. Biochimie. 2002. PMID: 12423794 Review.
-
Pyocins and Beyond: Exploring the World of Bacteriocins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Feb;17(1):240-252. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10322-3. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39023701 Review.
Cited by
-
MvaT negatively regulates pyocin S5 expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biotechnol Notes. 2022 Dec 9;3:102-107. doi: 10.1016/j.biotno.2022.11.004. eCollection 2022. Biotechnol Notes. 2022. PMID: 39416449 Free PMC article.
-
Draft genome sequence of the strain 16-537536, isolated from a patient with bronchiectasis and its relationship to the Pseudomonas koreensis group of the Pseudomonas fluorescens complex.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Jan 6;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4863-2. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 31907003 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of species-specific protein antibiotics in a murine model of acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 22;6:30201. doi: 10.1038/srep30201. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27444885 Free PMC article.
-
LlpB represents a second subclass of lectin-like bacteriocins.Microb Biotechnol. 2019 May;12(3):567-573. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13373. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Microb Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30702207 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and diversity of type VI secretion system clusters in Enterobacter bugandensis and Enterobacter cloacae.Microb Genom. 2023 Dec;9(12):001148. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001148. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 38054968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Vos, D. , Lim A. Jr, Pirnay J. P., Struelens M., Vandenvelde C., Duinslaeger L., et al. 1997. Direct detection and identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical samples such as skin biopsy specimens and expectorations by multiplex PCR based on two outer membrane lipoprotein genes, oprI and oprL . J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:1295–1299. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

