Mapping the Interaction Network of Key Proteins Involved in Histone mRNA Generation: A Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Study
- PMID: 26860583
- PMCID: PMC4847949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.01.031
Mapping the Interaction Network of Key Proteins Involved in Histone mRNA Generation: A Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Study
Abstract
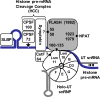
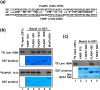
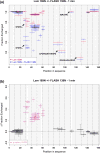
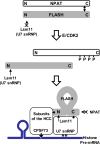
Histone pre-mRNAs are cleaved at the 3' end by a complex that contains U7 snRNP, the FLICE-associated huge protein (FLASH) and histone pre-mRNA cleavage complex (HCC) consisting of several polyadenylation factors. Within the complex, the N terminus of FLASH interacts with the N terminus of the U7 snRNP protein Lsm11, and together they recruit the HCC. FLASH through its distant C terminus independently interacts with the C-terminal SANT/Myb-like domain of nuclear protein, ataxia-telangiectasia locus (NPAT), a transcriptional co-activator required for expression of histone genes in S phase. To gain structural information on these interactions, we used mass spectrometry to monitor hydrogen/deuterium exchange in various regions of FLASH, Lsm11 and NPAT alone or in the presence of their respective binding partners. Our results indicate that the FLASH-interacting domain in Lsm11 is highly dynamic, while the more downstream region required for recruiting the HCC exchanges deuterium slowly and likely folds into a stable structure. In FLASH, a stable structure is adopted by the domain that interacts with Lsm11 and this domain is further stabilized by binding Lsm11. Notably, both hydrogen/deuterium exchange experiments and in vitro binding assays demonstrate that Lsm11, in addition to interacting with the N-terminal region of FLASH, also contacts the C-terminal SANT/Myb-like domain of FLASH, the same region that binds NPAT. However, while NPAT stabilizes this domain, Lsm11 causes its partial relaxation. These competing reactions may play a role in regulating histone gene expression in vivo.
Keywords: FLASH; Lsm11; Mass spectrometry; NPAT; U7 snRNP.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Marzluff WF. Metazoan replication-dependent histone mRNAs: a distinct set of RNA polymerase II transcripts. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:274–280. - PubMed
-
- Miele A, Braastad CD, Holmes WF, Mitra P, Medina R, Xie R, Zaidi SK, Ye X, Wei Y, Harper JW, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS. HiNF-P directly links the cyclin E/CDK2/p220NPAT pathway to histone H4 gene regulation at the G1/S phase cell cycle transition. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:6140–6153. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

