Exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases human hepatic stellate cell activation
- PMID: 26860701
- PMCID: PMC4792734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2016.02.001
Exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases human hepatic stellate cell activation
Abstract
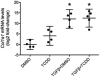
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon that elicits toxicity through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). In the liver, gross markers of TCDD toxicity are attributed to AhR activation in parenchymal hepatocytes. However, less is known regarding the consequences of TCDD treatment on non-parenchymal cells in the liver. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are non-parenchymal cells that store vitamin A when quiescent. Upon liver injury, activated HSCs lose this storage ability and instead function in the development and maintenance of inflammation and fibrosis through the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and collagen type I. Reports that TCDD exposure disrupts hepatic retinoid homeostasis and dysregulates extracellular matrix remodeling in the liver led us to speculate that TCDD treatment may disrupt HSC activity. The human HSC line LX-2 was used to test the hypothesis that TCDD treatment directly activates HSCs. Results indicate that exposure to 10nM TCDD almost completely inhibited lipid droplet storage in LX-2 cells cultured with retinol and palmitic acid. TCDD treatment also increased LX-2 cell proliferation, expression of α-smooth muscle actin, and production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), all of which are characteristics of activated HSCs. However, TCDD treatment had no effect on Col1a1 mRNA levels in LX-2 cells stimulated with the potent profibrogenic mediator, transforming growth factor-β. The TCDD-mediated increase in LX-2 cell proliferation, but not MCP-1 production, was abolished when phosphoinositide 3-kinase was inhibited. These results indicate that HSCs are susceptible to direct modulation by TCDD and that TCDD likely increases HSC activation through a multi-faceted mechanism.
Keywords: Collagen; Hepatic stellate cell; Liver; MCP-1; TCDD.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


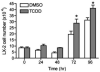
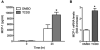

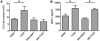
Similar articles
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases necroinflammation and hepatic stellate cell activation but does not exacerbate experimental liver fibrosis in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;311:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27693115 Free PMC article.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and liver fibrosis in C57BL6 mouse via activating Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2017 May 5;273:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28302560
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Prevents Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Liver Fibrogenesis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2019 Sep;157(3):793-806.e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.066. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31170413 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin cardiovascular embryotoxicity.Drug Metab Rev. 2006;38(1-2):261-89. doi: 10.1080/03602530600570099. Drug Metab Rev. 2006. PMID: 16684661 Review.
-
The stellate cell system (vitamin A-storing cell system).Anat Sci Int. 2017 Sep;92(4):387-455. doi: 10.1007/s12565-017-0395-9. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Anat Sci Int. 2017. PMID: 28299597 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 Nov 1;121:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 28506744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation by TCDD Modulates Expression of Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Genes during Experimental Liver Fibrosis.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5309328. doi: 10.1155/2016/5309328. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27672655 Free PMC article.
-
How single-cell transcriptomics provides insight on hepatic responses to TCDD.Curr Opin Toxicol. 2023 Dec;36:100441. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2023.100441. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37981901 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin increases the activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and is associated with the aggressiveness of osteosarcoma MG-63 osteoblast-like cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3849-3857. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9098. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127998 Free PMC article.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases necroinflammation and hepatic stellate cell activation but does not exacerbate experimental liver fibrosis in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;311:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27693115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham K, Krowke R, Neubert D. Pharmacokinetics And Biological-Activity Of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-Para-Dioxin .1. Dose-Dependent Tissue Distribution And Induction Of Hepatic Ethoxyresorufin O-Deethylase In Rats Following A Single Injection. Archives of Toxicology. 1988;62:359–368. - PubMed
-
- Black MB, Budinsky RA, Dombkowski A, Cukovic D, LeCluyse EL, Ferguson SS, Thomas RS, Rowlands JC. Cross-species Comparisons of Transcriptomic Alterations in Human and Rat Primary Hepatocytes Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicological Sciences. 2012;127:199–215. - PubMed
-
- Blaner WS, O'Byrne SM, Wongsiriroj N, Kluwe J, D'Ambrosio DM, Jiang HF, Schwabe RF, Hillman EMC, Piantedosi R, Libien J. Hepatic stellate cell lipid droplets: A specialized lipid droplet for retinoid storage. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2009;1791:467–473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blomhoff R, Rasmussen M, Nilsson A, Norum KR, Berg T, Blaner WS, Kato M, Mertz JR, Goodman DS, Eriksson U, Peterson PA. Hepatic Retinol Metabolism - Distribution Of Retinoids, Enzymes, And Binding-Proteins In Isolated Rat-Liver Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1985;260:3560–3565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

