An immunohistochemical study of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a possible prognostic biomarker
- PMID: 26860827
- PMCID: PMC4746778
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-016-0787-7
An immunohistochemical study of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a possible prognostic biomarker
Abstract
Background: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) is an atypical CDK which plays a vital role in several cancers via regulating migration and motility of cancer cells. However, the clinicopathological impact and function of CDK5 in lung cancer remain poorly understood. The present study was aimed at exploring expression and clinicopathological significance of CDK5 in lung cancer.
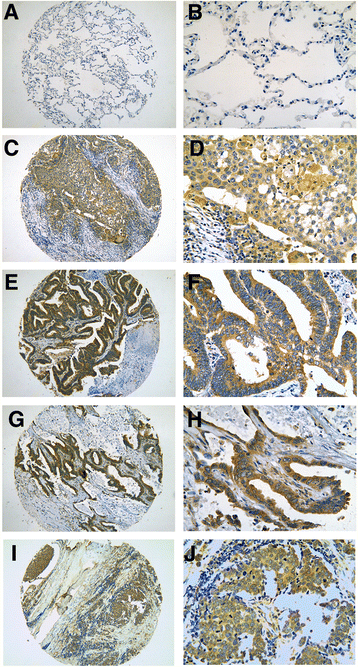
Methods: There were 395 samples of lung tissue including 365 lung tumors (339 non-small cell lung cancers and 26 small cell lung cancers) and 30 samples of normal lung. CDK5 expression was detected by immunohistochemistry on lung tissue microarrays.
Results: Over expression was detected in lung cancer compared with normal lung tissues (P=0.001). Furthermore, area under curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) of CDK5 was 0.685 (95% CI 0.564~0.751, P=0.004). In lung cancer, we also discovered close correlations between CDK5 and pathological grading (r=0.310, P<0.001), TNM stage (r=0.155, P=0.003), and lymph node metastasis (r=0.279, P<0.001) by using Spearman analysis. In two subgroups of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), the expression of CDK5 was also higher than that of normal lung tissue, respectively (P=0.001 and P=0.004). Moreover, in NSCLCs, Spearman analysis revealed that expression of CDK5 was correlated with TNM stages (r=0.129, P=0.017), lymph node metastasis (r=0.365, P<0.001), and pathological grading (r=0.307, P<0.001), respectively. The significant correlation was also found between CDK5 expression and TNM stages (r=0.415, P=0.049) and lymphatic metastasis (r=0.469, P=0.024) in SCLCs.
Conclusions: The results of this present study suggest that the CDK5 expression is associated with several clinicopathological factors linked with poorer prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 in lung cancer tissues.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(24):10591-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.24.10591. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25605144
-
HSP90B1 overexpression predicts poor prognosis in NSCLC patients.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):14321-14328. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5304-7. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27599983
-
Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 are metastatic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 10;16(1):876. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2903-z. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27832750 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of survivin expression in stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based therapy.Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;24(4):329-34. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26690822 Review.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of NM23 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Nov 24;100(47):e27919. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027919. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34964763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes the Progression of Colorectal Cancer Through Cdk5-Activated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 6;11:545251. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.545251. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33488528 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 44 inhibits cell growth by suppressing AKT signaling in non-small cell lung cancer.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 Sep;35(9):535-541. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12096. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31197957 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of CDK5 and their biological roles in cancer.Mol Biomed. 2021 Jul 20;2(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s43556-021-00029-0. Mol Biomed. 2021. PMID: 35006426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoprotein-based biomarkers as predictors for cancer therapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 4;117(31):18401-18411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010103117. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32690709 Free PMC article.
-
Immune system‑associated genes increase malignant progression and can be used to predict clinical outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2020 May;56(5):1199-1211. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.4998. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32319580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brothers JF, Hijazi K, Mascaux C, El-Zein RA, Spitz MR, Spira A. Bridging the clinical gaps: genetic, epigenetic and transcriptomic biomarkers for the early detection of lung cancer in the post-national lung screening trial era. BMC Med. 2013;11:168. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

