Effective treatment of HER2-amplified breast cancer by targeting HER3 and β1 integrin
- PMID: 26860947
- PMCID: PMC4767608
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3698-y
Effective treatment of HER2-amplified breast cancer by targeting HER3 and β1 integrin
Abstract
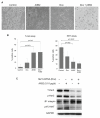
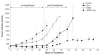
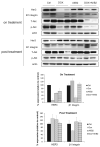
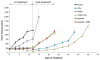
The central role of HER2 as the disease driver and HER3 as its essential partner has made them rational targets for the treatment of HER2-amplifed breast cancers, and there is considerable interest in developing highly effective treatment regimens for this disease that consist of targeted therapies alone. Much of these efforts are focused on dual targeting approaches, particularly dual targeting of the HER2-HER3 tumor driver complex itself, or vertical combinations that target downstream PI3K or Akt in addition to HER2. There is also potential in lateral combinations based on evidence implicating cross-talk with other membrane receptor systems, particularly integrins, and such lateral combinations can potentially involve either HER2 or HER3. We established a preclinical model of targeting HER3 using doxycycline-inducible shRNA and determined the efficacy of a β1 integrin inhibitor in combination with targeting HER3. We report that targeting HER3 and β1 integrin provides a particularly effective combination therapy approach for HER2-amplified cancers, surpassing the combination of HER2 and β1 integrin targeting, and evading some of the safety concerns associated with direct HER2-targeting. This further validates HER3 as a major hub mediating the tumorigenic functions of HER2 and identifies it as a high value target for lateral combination therapy strategies.
Keywords: AIIB2; Combination therapy; HER2; HER3; OS2966; β1 integrin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical probing of HER2-amplified cancer cells identifies TORC2 as a particularly effective secondary target for combination with lapatinib.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):41123-33. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5660. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26516700 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody targeting of HER2/HER3 signaling overcomes heregulin-induced resistance to PI3K inhibition in prostate cancer.Int J Cancer. 2015 Jul 15;137(2):267-77. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29378. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25471734
-
hMENA(11a) contributes to HER3-mediated resistance to PI3K inhibitors in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 18;35(7):887-96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.143. Epub 2015 May 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25961924
-
Targeting HER family in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: potential biomarkers and novel targeted therapies.Pharmacogenomics. 2015;16(3):257-71. doi: 10.2217/pgs.14.133. Pharmacogenomics. 2015. PMID: 25712189 Review.
-
Targeting HER proteins in cancer therapy and the role of the non-target HER3.Br J Cancer. 2007 Aug 20;97(4):453-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603910. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17667926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Therapeutic Efficacy of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus-1 with Integrin β1 Blocking Antibody OS2966.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Jun;18(6):1127-1136. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0953. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30926634 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Integrins in Resistance to Therapies Targeting Growth Factor Receptors in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 17;11(5):692. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050692. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31109009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond adhesion: emerging roles for integrins in control of the tumor microenvironment.F1000Res. 2017 Aug 31;6:1612. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11877.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 29026524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Cohesive Cluster Phenotype in Chordoma via β1 Integrin Increases Ionizing Radiation Efficacy.Neoplasia. 2017 Nov;19(11):919-927. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 24. Neoplasia. 2017. PMID: 28954241 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of PAbs generated by immunization with a novel HER3-targeting protein-based vaccine candidate in preclinical models.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 16;14:1472607. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1472607. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39479017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19(56):6550–6565. - PubMed
-
- Wieduwilt MJ, Moasser MM. The epidermal growth factor receptor family: biology driving targeted therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65(10):1566–1584. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-7440-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA. Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(1):9–22. doi: 10.1038/nrc2748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rathinam R, Alahari SK. Important role of integrins in the cancer biology. Cancer metastasis reviews. 2010;29(1):223–237. doi: 10.1007/s10555-010-9211-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cox D, Brennan M, Moran N. Integrins as therapeutic targets: lessons and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9(10):804–820. doi: 10.1038/nrd3266. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

