A herbal formula comprising Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos, attenuates collagen-induced arthritis and inhibits TLR4 signalling in rats
- PMID: 26860973
- PMCID: PMC4748217
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20042
A herbal formula comprising Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos, attenuates collagen-induced arthritis and inhibits TLR4 signalling in rats
Abstract
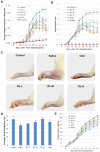
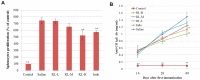
RL, a traditional remedy for Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), comprises two edible herbs, Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. We have reported that RL could inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators in immune cells. Here we investigated the effects and the mechanism of action of RL in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. RL significantly increased food intake and weight gain of CIA rats without any observable adverse effect; ameliorated joint erythema and swelling; inhibited immune cell infiltration, bone erosion and osteophyte formation in joints; reduced joint protein expression levels of TLR4, phospho-TAK1, phospho-NF-κB p65, phospho-c-Jun and phospho-IRF3; lowered levels of inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17A and MCP-1 in sera and TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-17A in joints); elevated serum IL-10 level; reinvigorated activities of antioxidant SOD, CAT and GSH-Px in the liver and serum; reduced Th17 cell proportions in splenocytes; inhibited splenocyte proliferation and activation; and lowered serum IgG level. In conclusion, RL at nontoxic doses inhibited TLR4 signaling and potently improved clinical conditions of CIA rats. These findings provide further pharmacological justifications for the traditional use of RL in RA management.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A herbal formula comprising Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators and the IRAK-1/TAK1 and TBK1/IRF3 pathways in RAW 264.7 and THP-1 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:195-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26297845
-
A herbal formula consisting of Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos inhibits inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 14;153(3):922-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.029. Epub 2014 Feb 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24568773
-
An herbal formula inhibits STAT3 signaling and attenuates bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis rats.Phytomedicine. 2020 Sep;76:153254. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153254. Epub 2020 May 30. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32531698
-
Pharmacological Activities of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Its Derivative-"Chrysoeriol" in Skin Diseases.Molecules. 2024 Apr 25;29(9):1972. doi: 10.3390/molecules29091972. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genus Rosa and arthritis: Overview on pharmacological perspectives.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Dec;114:219-234. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.10.029. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27816506 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Qianghuo Erhuang Decoction on T Regulatory and T Helper 17 Cells in Treatment of Adjuvant-induced Arthritis in Rats.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 8;7(1):17198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17566-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29222448 Free PMC article.
-
Oral treatment with Rosa multiflora fructus extract modulates mast cells in canine atopic dermatitis.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 9;12:1531313. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1531313. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40271492 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Delivery of Teriflunomide and Methotrexate from Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: In Vitro Characterization, Pharmacodynamic and Biochemical Investigations.Pharm Res. 2018 Sep 5;35(11):201. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2478-2. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30187188
-
The Role of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants against Obesity and Arthritis: A Review.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 25;14(5):985. doi: 10.3390/nu14050985. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35267958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Correlation of IgG4 and IL-21 in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rats.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Oct 1;14:5051-5058. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S317420. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34629885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mok C. C., Kwok C. L., Ho L. Y., Chan P. T. & Yip S. F. Life expectancy, standardized mortality ratios, and causes of death in six rheumatic diseases in Hong Kong, China. Arthritis Rheum 63, 1182–1189 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Adams K., Bombardier C. & van der Heijde D. Safety and efficacy of on-demand versus continuous use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in patients with inflammatory arthritis: a systematic literature review. J Rheumatol Suppl 90, 56–58 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Goh F. G. & Midwood K. S. Intrinsic danger: activation of Toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51, 7–23 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Ospelt C. et al.. Overexpression of toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: toll-like receptor expression in early and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58, 3684–3692 (2008). - PubMed
-
- van der Heijden I. M. et al.. Presence of bacterial DNA and bacterial peptidoglycans in joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthritides. Arthritis Rheum 43, 593–598 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

