SpyRing interrogation: analyzing how enzyme resilience can be achieved with phytase and distinct cyclization chemistries
- PMID: 26861173
- PMCID: PMC4748275
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21151
SpyRing interrogation: analyzing how enzyme resilience can be achieved with phytase and distinct cyclization chemistries
Abstract
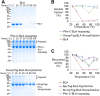
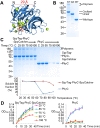
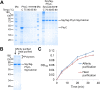
Enzymes catalyze reactions with exceptional selectivity and rate acceleration but are often limited by instability. Towards a generic route to thermo-resilience, we established the SpyRing approach, cyclizing enzymes by sandwiching between SpyTag and SpyCatcher (peptide and protein partners which lock together via a spontaneous isopeptide bond). Here we first investigated the basis for this resilience, comparing alternative reactive peptide/protein pairs we engineered from Gram-positive bacteria. Both SnoopRing and PilinRing cyclization gave dramatic enzyme resilience, but SpyRing cyclization was the best. Differential scanning calorimetry for each ring showed that cyclization did not inhibit unfolding of the inserted β-lactamase. Cyclization conferred resilience even at 100 °C, where the cyclizing domains themselves were unfolded. Phytases hydrolyze phytic acid and improve dietary absorption of phosphate and essential metal ions, important for agriculture and with potential against human malnutrition. SpyRing phytase (PhyC) resisted aggregation and retained catalytic activity even following heating at 100 °C. In addition, SpyRing cyclization made it possible to purify phytase simply by heating the cell lysate, to drive aggregation of non-cyclized proteins. Cyclization via domains forming spontaneous isopeptide bonds is a general strategy to generate resilient enzymes and may extend the range of conditions for isolation and application of enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
M.H. is an inventor on a patent concerning peptide reaction via spontaneous amide bond formation (EP2534484).
Figures



References
-
- Kawedia J. D. & Rytting M. E. Asparaginase in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 14, Supplement, S14–S17 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Reetz M. T. & Carballeira J. D. Iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) for rapid directed evolution of functional enzymes. Nat. Protoc. 2, 891–903 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Evans T. C. Jr, Benner J. & Xu M. Q. The in vitro ligation of bacterially expressed proteins using an intein from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 3923–3926 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Iwai H. & Plückthun A. Circular β-lactamase: stability enhancement by cyclizing the backbone. FEBS Lett. 459, 166–172 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

