Metformin improves the angiogenic potential of human CD34⁺ cells co-incident with downregulating CXCL10 and TIMP1 gene expression and increasing VEGFA under hyperglycemia and hypoxia within a therapeutic window for myocardial infarction
- PMID: 26861446
- PMCID: PMC4748498
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-016-0344-2
Metformin improves the angiogenic potential of human CD34⁺ cells co-incident with downregulating CXCL10 and TIMP1 gene expression and increasing VEGFA under hyperglycemia and hypoxia within a therapeutic window for myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). To identify the most effective treatment for CVD, it is paramount to understand the mechanism behind cardioprotective therapies. Although metformin has been shown to reduce CVD in Type-2 DM clinical trials, the underlying mechanism remains unexplored. CD34(+) cell-based therapies offer a new treatment approach to CVD. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of metformin on the angiogenic properties of CD34(+) cells under conditions mimicking acute myocardial infarction in diabetes.
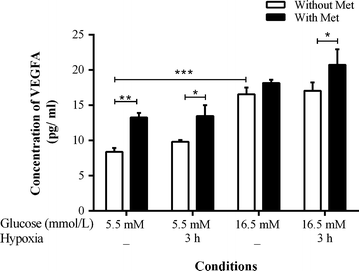
Methods: CD34(+) cells were cultured in 5.5 or 16.5 mmol/L glucose ± 0.01 mmol/L metformin and then additionally ± 4 % hypoxia. The paracrine function of CD34(+) cell-derived conditioned medium was assessed by measuring pro-inflammatory cytokines, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), and using an in vitro tube formation assay for angiogenesis. Also, mRNA of CD34(+) cells was assayed by microarray and genes of interest were validated by qRT-PCR.
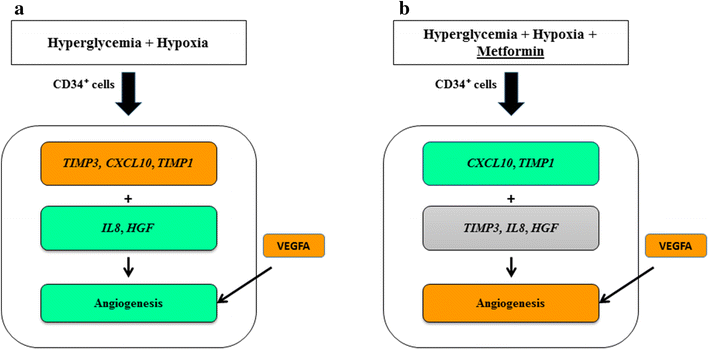
Results: Metformin increased in vitro angiogenesis under hyperglycemia-hypoxia and augmented the expression of VEGFA. It also reduced the angiogenic-inhibitors, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 (CXCL10) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1) mRNAs, which were upregulated under hyperglycemia-hypoxia. In addition metformin, increased expression of STEAP family member 4 (STEAP4) under euglycemia, indicating an anti-inflammatory effect.
Conclusions: Metformin has a dual effect by simultaneously increasing VEGFA and reducing CXCL10 and TIMP1 in CD34(+) cells in a model of the diabetic state combined with hypoxia. Therefore, these angiogenic inhibitors are promising therapeutic targets for CVD in diabetic patients. Moreover, our data are commensurate with a vascular protective effect of metformin and add to the understanding of underlying mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proangiogenic Effect of Metformin in Endothelial Cells Is via Upregulation of VEGFR1/2 and Their Signaling under Hyperglycemia-Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 19;19(1):293. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010293. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29351188 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of combined treatment with rosuvastatin and protein kinase Cβ2 inhibitor on angiogenesis following myocardial infarction in diabetic rats.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Mar;35(3):829-38. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2043. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25524396
-
Testosterone replacement therapy promotes angiogenesis after acute myocardial infarction by enhancing expression of cytokines HIF-1a, SDF-1a and VEGF.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 5;684(1-3):116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.03.032. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22484505
-
CD34-positive stem cells: in the treatment of heart and vascular disease in human beings.Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(5):474-85. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011. PMID: 22163120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of action of metformin and its regulatory effect on microRNAs related to angiogenesis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Feb;164:105390. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105390. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33352227 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of angiogenesis pattern and related immune landscape for individual treatment in osteosarcoma.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Jun 29;7(1):62. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00415-7. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37386055 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from bariatric surgery: Can increased GLP-1 enhance vascular repair during cardiometabolic-based chronic disease?Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Dec;22(4):1171-1188. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09669-7. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34228302 Review.
-
Metformin: The next angiogenesis panacea?SAGE Open Med. 2021 Mar 16;9:20503121211001641. doi: 10.1177/20503121211001641. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med. 2021. PMID: 33796300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Angiogenic miR-222, miR-195, and miR-21a Plasma Levels in T1DM Are Improved by Metformin Therapy, Thus Elucidating Its Cardioprotective Effect: The MERIT Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 19;19(10):3242. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103242. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347712 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Progenitor Cells Dysfunctions and Cardiometabolic Disorders: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 22;22(13):6667. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136667. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206404 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization. WH: WHO mortality database—January 2015 update. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/.
-
- Federation ID: IDF Diabetes Atlas 6th edition-2013. https://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/EN_6E_Atlas_Full_0pdf.
-
- Piccolo R, Galasso G, Iversen AZ, Eitel I, Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Gu YL, de Smet BJ, Mahmoud KD, Abreu-Gonzalez P, Trimarco B, et al. Effects of baseline coronary occlusion and diabetes mellitus in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2014;114(8):1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.07.030. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

