Recent advances in microvascular autologous breast reconstruction after ablative tumor surgery
- PMID: 26862495
- PMCID: PMC4734933
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v7.i1.114
Recent advances in microvascular autologous breast reconstruction after ablative tumor surgery
Abstract
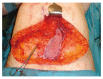
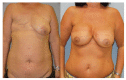
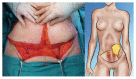
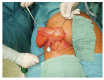
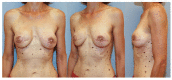
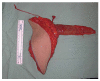
Breast cancer is a ubiquitous disease and one of the leading causes of death in women in western societies. With overall increasing survival rates, the number of patients who need post-mastectomy reconstruction is on the rise. Especially since its psychological benefits have been broadly recognized, breast reconstruction has become a key component of breast cancer treatment. Evolving from the early beginnings of breast reconstruction with synthetic implants in the 1960s, microsurgical tissue transfer is on the way to become the gold standard for post oncology restoration of the breast. Particularly since the advent of perforator based free flap surgery, free tissue transfer has become as safe option for breast reconstruction with low morbidity. The lower abdominal skin and subcutaneous fat tissue typically offer enough volume to create an aesthetically satisfying breast mound. Nowadays, the most commonly used flap from this donor site is the deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap. If the lower abdomen is not available as a donor site, the gluteal area and thigh provide a number of flaps suitable for breast reconstruction. If the required breast volume is small, and there is enough tissue available on the upper medial thigh, then a transverse upper gracilis flap may be a practicable method to reconstruct the breast. In case of a higher amount of required volume, a gluteal artery perforator flap is the best choice. However, what is crucial in addition to selecting the best flap option for the individual patient is the timing of the operation. In patients with confirmed post-mastectomy radiation therapy, it is advisable to perform microvascular breast reconstruction only in a delayed fashion.
Keywords: Autologous tissue transfer; Breast cancer; Breast reconstruction; Deep inferior epigastric perforator; Fasciocutaneous infragluteal; Flap; Microsurgery; Transverse musculocutaneous gracilis.
Figures





References
-
- Iwuchukwu OC, Harvey JR, Dordea M, Critchley AC, Drew PJ. The role of oncoplastic therapeutic mammoplasty in breast cancer surgery--a review. Surg Oncol. 2012;21:133–141. - PubMed
-
- Berry MG, Fitoussi AD, Curnier A, Couturaud B, Salmon RJ. Oncoplastic breast surgery: a review and systematic approach. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63:1233–1243. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin SA. Surgical management of the breast: breast conservation therapy and mastectomy. Surg Clin North Am. 2013;93:411–428. - PubMed
-
- Noone RB. Thirty-five years of breast reconstruction: eleven lessons to share. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:1820–1827. - PubMed
-
- Preminger BA, Lemaine V, Sulimanoff I, Pusic AL, McCarthy CM. Preoperative patient education for breast reconstruction: a systematic review of the literature. J Cancer Educ. 2011;26:270–276. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

