The mechanism of acquired resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients
- PMID: 26862733
- PMCID: PMC4914294
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7189
The mechanism of acquired resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Abstract
Introduction: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are associated with favorable response in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Acquired resistance to reversible EGFR TKIs remains a significant barrier, and acquired EGFR T790M-mutation is the major mechanism. Second-generation irreversible EGFR TKI, afatinib, had also been approved for treating EGFR mutant lung cancer patients, but the mechanism of acquired resistance to afatinib has not been well studied.
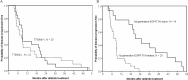
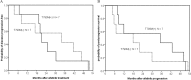
Results: Forty-two patients had tissue specimens taken after acquiring resistance to afatinib. The sensitizing EGFR mutation were all consistent between pre- and post-afatinib tissues. Twenty patients (47.6%) had acquired T790M mutation. T790M rate was not different between first-generation EGFR TKI-naïve patients (50%) and first-generation EGFR TKI-treated patients (46.4%) (p = 0.827). No clinical characteristics or EGFR mutation types were associated with the development of acquired T790M. No other second-site EGFR mutations were detected. There were no small cell or squamous cell lung cancer transformation. Other genetic mutations were not identified in PIK3CA, BRAF, HER2, KRAS, NRAS, MEK1, AKT2, LKB1 and JAK2.
Methods: Afatinib-prescription record of our department of pharmacy from January 2007 and December 2014 was retrieved. We investigated patients with tissue specimens available after acquiring resistance to afatinib. Enrolled patients should have partial response or durable stable disease of treatment response to afatinib. Various mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-generation EGFR TKIs were evaluated. Histology and cytology were reviewed. EGFR, PIK3CA, BRAF, HER2, KRAS, NRAS, MEK1, AKT2, LKB1 and JAK2 genetic alterations were evaluated by sequencing. Statistical analysis was performed using Chi-square test and Kaplan-Meier method.
Conclusions: T790M was detected in half of the lung adenocarcinoma after acquiring resistance to afatinib. T790M is still the major acquired resistance mechanism. First-generation EGFR TKI exposure did not influence the prevalence of T790M in lung cancer acquired resistance to afatinib.
Keywords: EGFR TKI; T790M; acquired resistance; afatinib; lung adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Yu, Dr. C-H Yang and Dr. Shih received honoraria for speeches from Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2014. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. The New England journal of medicine. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. The Lancet Oncology. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2010;11:121–128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

