Reduced RKIP enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity
- PMID: 26862850
- PMCID: PMC4905486
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7201
Reduced RKIP enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity
Abstract
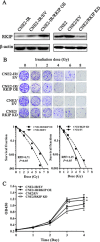
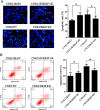
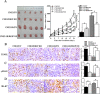
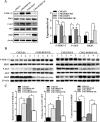
Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) functions as a chemo-immunotherapeutic sensitizer of cancers, but regulation of RKIP on tumor radiosensitivity remains largely unexplored. In this study, we investigate the role and mechanism of RKIP in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) radioresistance. The results showed that RKIP was frequently downregulated in the radioresistant NPC tissues compared with radiosensitive NPC tissues, and its reduction correlated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient survival, and was an independent prognostic factor. In vitro radioresponse assay showed that RKIP overexpression decreased while RKIP knockdown increased NPC cell radioresistance. In the NPC xenografts, RKIP overexpression decreased while RKIP knockdown increased tumor radioresistance. Mechanistically, RKIP reduction promoted NPC cell radioresistance by increasing ERK and AKT activity, and AKT may be a downstream transducer of ERK signaling. Moreover, the levels of phospho-ERK-1/2 and phospho-AKT were increased in the radioresistant NPC tissues compared with radiosensitive ones, and negatively associated with RKIP expression, indicating that RKIP-regulated NPC radioresponse is mediated by ERK and AKT signaling in the clinical samples. Our data demonstrate that RKIP is a critical determinant of NPC radioresponse, and its reduction enhances NPC radioresistance through increasing ERK and AKT signaling activity, highlighting the therapeutic potential of RKIP-ERK-AKT signaling axis in NPC radiosensitization.
Keywords: AKT; ERK−1/2; RKIP; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Poon Y, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, Chan DK, Tung SY, Thaw M, Ho JH. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976–1985: overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C, Fee F, Katsanakis KD, Rose DW, Mischak H, Sedivy JM, Kolch W. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 1999;401:173–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

