Plankton networks driving carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean
- PMID: 26863193
- PMCID: PMC4851848
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16942
Plankton networks driving carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean
Abstract
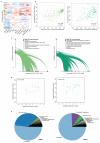
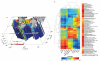
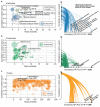
The biological carbon pump is the process by which CO2 is transformed to organic carbon via photosynthesis, exported through sinking particles, and finally sequestered in the deep ocean. While the intensity of the pump correlates with plankton community composition, the underlying ecosystem structure driving the process remains largely uncharacterized. Here we use environmental and metagenomic data gathered during the Tara Oceans expedition to improve our understanding of carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean. We show that specific plankton communities, from the surface and deep chlorophyll maximum, correlate with carbon export at 150 m and highlight unexpected taxa such as Radiolaria and alveolate parasites, as well as Synechococcus and their phages, as lineages most strongly associated with carbon export in the subtropical, nutrient-depleted, oligotrophic ocean. Additionally, we show that the relative abundance of a few bacterial and viral genes can predict a significant fraction of the variability in carbon export in these regions.
Figures






Comment in
-
Environmental microbiology: Pumping carbon to the deep ocean.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Apr;14(4):194. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.29. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26898365 No abstract available.
-
Ocean science: The rise of Rhizaria.Nature. 2016 Apr 28;532(7600):444-5. doi: 10.1038/nature17892. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27096370 No abstract available.
References
-
- Field CB, Behrenfeld MJ, Randerson JT, Falkowski P. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science. 1998;281:237–240. doi:10.1126/Science.281.5374.237. - PubMed
-
- Boyd PW, Newton P. Evidence of the potential Influence of planktonic community structure on the interannual variability of particulate organic-carbon flux. Deep-Sea Res. I. 1995;42:619–639.
-
- Guidi L, et al. Effects of phytoplankton community on production, size, and export of large aggregates: A world-ocean analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009;54:1951–1963.
-
- Kwon EY, Primeau F, Sarmiento JL. The impact of remineralization depth on the air-sea carbon balance. Nat Geosci. 2009;2:630–635.
-
- IPCC . Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

