The dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA
- PMID: 26863196
- PMCID: PMC4842015
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16998
The dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA
Abstract
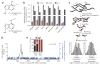
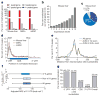
Gene expression can be regulated post-transcriptionally through dynamic and reversible RNA modifications. A recent noteworthy example is N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A), which affects messenger RNA (mRNA) localization, stability, translation and splicing. Here we report on a new mRNA modification, N(1)-methyladenosine (m(1)A), that occurs on thousands of different gene transcripts in eukaryotic cells, from yeast to mammals, at an estimated average transcript stoichiometry of 20% in humans. Employing newly developed sequencing approaches, we show that m(1)A is enriched around the start codon upstream of the first splice site: it preferentially decorates more structured regions around canonical and alternative translation initiation sites, is dynamic in response to physiological conditions, and correlates positively with protein production. These unique features are highly conserved in mouse and human cells, strongly indicating a functional role for m(1)A in promoting translation of methylated mRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures














Comment in
-
Epigenetics: A new methyl mark on messengers.Nature. 2016 Feb 25;530(7591):423-4. doi: 10.1038/530423a. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26911777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

