LEADER 5: prevalence and cardiometabolic impact of obesity in cardiovascular high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: baseline global data from the LEADER trial
- PMID: 26864124
- PMCID: PMC4750199
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-016-0341-5
LEADER 5: prevalence and cardiometabolic impact of obesity in cardiovascular high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: baseline global data from the LEADER trial
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological data on obesity are needed, particularly in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and high cardiovascular (CV) risk. We used the baseline data of liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: evaluation of CV outcome results-A long term Evaluation (LEADER) (a clinical trial to assess the CV safety of liraglutide) to investigate: (i) prevalence of overweight and obesity; (ii) relationship of the major cardiometabolic risk factors with anthropometric measures of adiposity [body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC)]; and (iii) cardiometabolic treatment intensity in relation to BMI and WC.
Methods: LEADER enrolled two distinct populations of high-risk patients with T2DM in 32 countries: (1) aged ≥50 years with prior CV disease; (2) aged ≥60 years with one or more CV risk factors. Associations of metabolic variables, demographic variables and treatment intensity with anthropometric measurements (BMI and WC) were explored using regression models (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01179048).
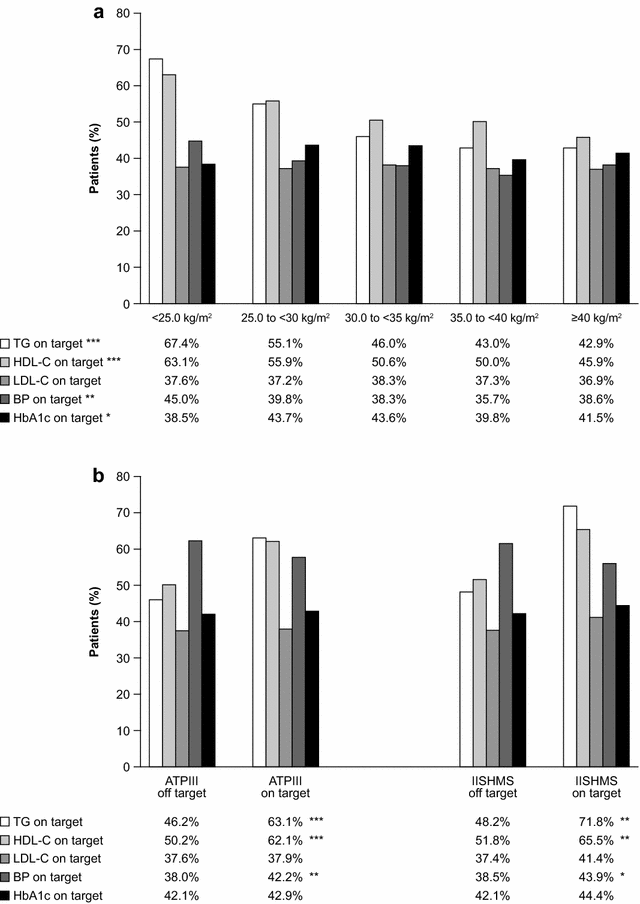
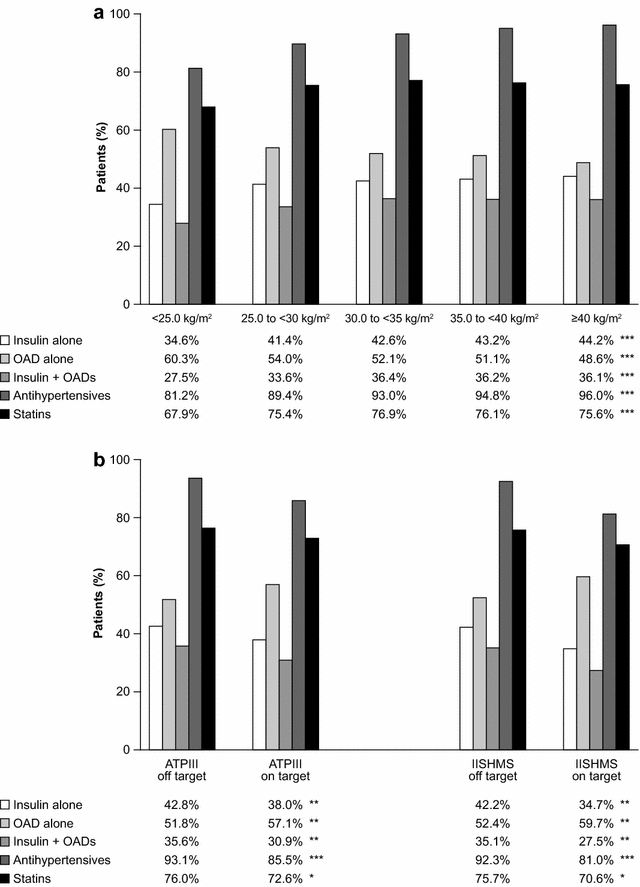
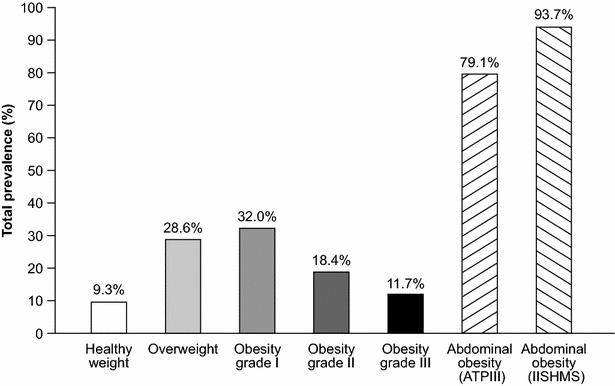
Results: Mean BMI was 32.5 ± 6.3 kg/m(2) and only 9.1 % had BMI <25 kg/m(2). The prevalence of healthy WC was also extremely low (6.4 % according to International Joint Interim Statement for the Harmonization of the Metabolic Syndrome criteria). Obesity was associated with being younger, female, previous smoker, Caucasian, American, with shorter diabetes duration, uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), antihypertensive agents, insulin plus oral antihyperglycaemic treatment, higher levels of triglycerides and lower levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Conclusions: Overweight and obesity are prevalent in high CV risk patients with T2DM. BMI and WC are related to the major cardiometabolic risk factors. Furthermore, treatment intensity, such as insulin, statins or oral antihypertensive drugs, is higher in those who are overweight or obese; while BP and lipid control in these patients are remarkably suboptimal. LEADER confers a unique opportunity to explore the longitudinal effect of weight on CV risk factors and hard endpoints.
Figures
References
-
- Bhan V, Yan RT, Leiter LA, Fitchett DH, Langer A, Lonn E, et al. Guidelines oriented approach in lipid lowering (GOALL) registry and vascular protection (VP) registry investigators. Relation between obesity and the attainment of optimal blood pressure and lipid targets in high vascular risk outpatients. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106:1270–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.06.055. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

