The role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in autoimmunity and implications for therapy
- PMID: 26864273
- PMCID: PMC5070917
- DOI: 10.1586/1744666X.2016.1152888
The role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in autoimmunity and implications for therapy
Abstract
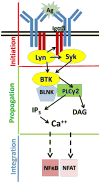
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) mediates B cell signaling and is also present in innate immune cells but not T cells. BTK propagates B cell receptor (BCR) responses to antigen-engagement as well as to stimulation via CD40, toll-like receptors (TLRs), Fc receptors (FCRs) and chemokine receptors. Importantly, BTK can modulate signaling, acting as a "rheostat" rather than an "on-off" switch; thus, overexpression leads to autoimmunity while decreased levels improve autoimmune disease outcomes. Autoreactive B cells depend upon BTK for survival to a greater degree than normal B cells, reflected as loss of autoantibodies with maintenance of total antibody levels when BTK is absent. This review describes contributions of BTK to immune tolerance, including studies testing BTK-inhibitors for treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: B lymphocyte signaling; BTK inhibitors; Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; autoimmune inflammatory arthritis; autoimmunity; systemic lupus erythematosus; type 1 diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Bruton OC. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952;9:722–8. First report describing humoral immunodeficiency in a male child with a disease later termed x-linked agammablobulinemia (XLA) and attributed to Bruton’s tyrosine kinase difficiency. - PubMed
-
- Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Lederman HM, Jones SM, Sullivan K, Burks AW, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Ochs HD. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: report on a United States registry of 201 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006;85:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Howard V, Greene JM, Pahwa S, Winkelstein JA, Boyle JM, Kocak M, Conley ME. The health status and quality of life of adults with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clinical immunology. 2006;118:201–8. - PubMed
-
- Vetrie D, Vorechovsky I, Sideras P, Holland J, Davies A, Flinter F, Hammarstrom L, Kinnon C, Levinsky R, Bobrow M, et al. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993;361:226–33. The first of two seminal papers identifying the B cell tyrosine kinase deficient in XLA, later named Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada S, Saffran DC, Rawlings DJ, Parolini O, Allen RC, Klisak I, Sparkes RS, Kubagawa H, Mohandas T, Quan S, et al. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993;72:279–90. One of two seminal papers identifying B cell tyrosine kinase deficient in XLA, later named Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
