Synthesis of Capped A(II)B(VI) Nanoparticles for Fluorescent Biomarkers
- PMID: 26864278
- PMCID: PMC4749517
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-016-1300-5
Synthesis of Capped A(II)B(VI) Nanoparticles for Fluorescent Biomarkers
Abstract
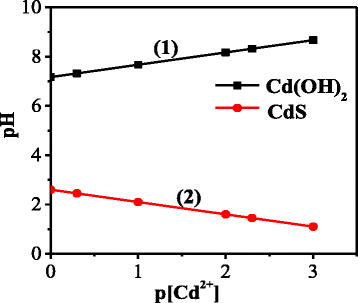
The conditions for growing CdS nanoparticles suitable for the visualization of biological tissues were theoretically studied and experimentally checked. The optimal ranges for pH values and precursors' concentrations were determined. The applicability of the mercaptoethanol-capped nanoparticles for in vitro luminescence visualization of several cellular forms in histological specimens of human placenta has been proven.
Keywords: Biomarker; CdS; Fluorescence; Mercaptoethanol; Nanoparticles.
Figures




References
-
- Linga D, Hacketta MJ, Hyeon T. Surface ligands in synthesis, modification, assembly and biomedical applications of nanoparticles. Nanotoday. 2014;9(4):457–477. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.06.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

