PERK Integrates Oncogenic Signaling and Cell Survival During Cancer Development
- PMID: 26864318
- PMCID: PMC4912452
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25336
PERK Integrates Oncogenic Signaling and Cell Survival During Cancer Development
Abstract
Unfolded protein responses (UPR), consisting of three major transducers PERK, IRE1, and ATF6, occur in the midst of a variety of intracellular and extracellular challenges that perturb protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). ER stress occurs and is thought to be a contributing factor to a number of human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and various metabolic syndromes. In the context of neoplastic growth, oncogenic stress resulting from dysregulation of oncogenes such as c-Myc, Braf(V600E) , and HRAS(G12V) trigger the UPR as an adaptive strategy for cancer cell survival. PERK is an ER resident type I protein kinase harboring both pro-apoptotic and pro-survival capabilities. PERK, as a coordinator through its downstream substrates, reprograms cancer gene expression to facilitate survival in response to oncogenes and microenvironmental challenges, such as hypoxia, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Herein, we discuss how PERK kinase engages in tumor initiation, transformation, adaption microenvironmental stress, chemoresistance and potential opportunities, and potential opportunities for PERK targeted therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 231: 2088-2096, 2016. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

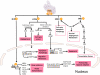
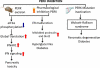
References
-
- Amaravadi RK, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yin XM, Weiss WA, Takebe N, Timmer W, DiPaola RS, Lotze MT, White E. Principles and current strategies for targeting autophagy for cancer treatment. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2011;17:654–666. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkins C, Liu Q, Minthorn E, Zhang SY, Figueroa DJ, Moss K, Stanley TB, Sanders B, Goetz A, Gaul N, et al. Characterization of a novel PERK kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer research. 2013;73:1993–2002. - PubMed
-
- Axten JM, Medina JR, Feng Y, Shu A, Romeril SP, Grant SW, Li WH, Heerding DA, Minthorn E, Mencken T, et al. Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-p yrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2012;55:7193–7207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

