Microbial communities affecting albumen photography heritage: a methodological survey
- PMID: 26864429
- PMCID: PMC4749957
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20810
Microbial communities affecting albumen photography heritage: a methodological survey
Abstract
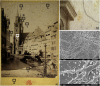
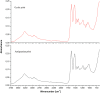
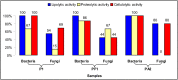
This study is one of the few investigations which analyze albumen prints, perhaps the most important photographic heritage of the late 19(th) and early 20(th) centuries. The chemical composition of photographic samples was assessed using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray fluorescence. These two non-invasive techniques revealed the complex nature of albumen prints, which are composed of a mixture of proteins, cellulose and salts. Microbial sampling was performed using cellulose nitrate membranes which also permitted the trapped microflora to be observed with a scanning electron microscope. Microbial analysis was performed using the combination of culture-dependent (cultivation in different media, including one 3% NaCl) and culture-independent (bacterial and fungal cloning and sequencing) approaches. The isolated microorganisms were screened for their lipolytic, proteolytic, cellulolytic, catalase and peroxidase activities. The combination of the culture-dependent and -independent techniques together with enzymatic assays revealed a substantial microbial diversity with several deteriogen microorganisms from the genera Bacillus, Kocuria, Streptomyces and Geobacillus and the fungal strains Acrostalagmus luteoalbus, Bjerkandera adusta, Pleurotus pulmonarius and Trichothecium roseum.
Figures



References
-
- Marien M. W. Photography: A cultural history. Laurence King Publishing (2006).
-
- Reilly J. M. & McCabe C. Care and identification of 19th century photographic prints. Eastman Kodak Company (1986).
-
- Cappitelli F. & Sorlini C. From papyrus to compact disc: the microbial deterioration of documentary heritage. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 31, 1–10 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Sterflinger K. & Pinzari F. The revenge of time: fungal deterioration of cultural heritage with particular reference to books, paper and parchment. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 559–566 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

