Simultaneous development of sarcoidosis and cutaneous vasculitis in a patient with refractory Crohn's disease during infliximab therapy
- PMID: 26864464
- PMCID: PMC4750217
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-016-0193-5
Simultaneous development of sarcoidosis and cutaneous vasculitis in a patient with refractory Crohn's disease during infliximab therapy
Abstract
Background: Paradoxical inflammations during anti-TNF-α therapy are defined as adverse effects such as psoriasiform skin lesions, uveitis and sarcoidosis-like granulomas induced by immune reactions, not by infectious agents. Here, we report a very rare case of the simultaneous development of sarcoidosis and cutaneous vasculitis in a patient with refractory Crohn's disease during infliximab therapy and both of which resolved spontaneously without the cessation of infliximab.
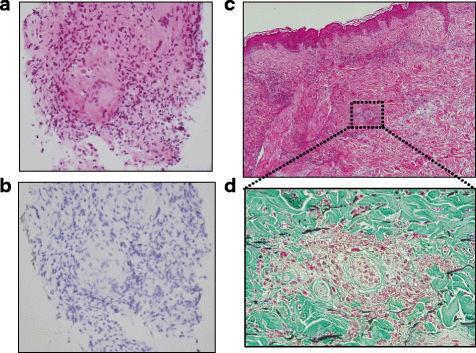
Case presentation: In September 2000, 23-year old Japanese male was diagnosed with Crohn's disease. Prednisolone in combination with mesalazine was introduced at first and succeeded for almost one year. In June 2002, since his gastrointestinal symptoms relapsed and were refractory, infliximab (IFX) therapy 5 mg/kg was introduced. In February 2011, because he had repeated arthralgia almost every intravenous IFX administration, IFX was increased to 10 mg/kg under the diagnosis of a secondary failure of IFX. In December 2012, he complained of slight dry cough and an itchy eruption on both lower limbs, and he was referred to our hospital due to the appearance of bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on chest X-ray examination. Chest computed tomogram revealed bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and fine reticulonodular shadows on the bilateral upper lungs. Serum calcium, angiotensin-converting enzyme and soluble interleukin 2 receptor levels were not elevated, but the titer of antinuclear antibody was considerably elevated. Mycobacterium infection was carefully excluded. Trans-bronchial lung biopsy showed non-caseating epithelioid cell granulomas compatible with sarcoidosis. The skin biopsy of the right limb was diagnosed as leukocytoclastic vasculitis. The patient was diagnosed as having a series of paradoxical inflammations during anti-TNF-α therapy. Since his paradoxical inflammations were not severe and opportunistic infections were excluded, IFX was cautiously continued for refractory Crohn's disease. Nine months later, not only his intrathoracic lesions but also his cutaneous lesions had spontaneously resolved.
Conclusion: Physicians caring for patients with anti-TNF-α therapy should know that, based on a careful exclusion of infectious agents and thoughtful assessment of the patient's possible risks and benefits, paradoxical inflammations can be resolved without the cessation of anti-TNF-α therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type B in a Patient with Crohn's Disease Treated with TNF-Alpha Inhibitors Infliximab and Adalimumab.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019 Sep;27(3):202-204. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019. PMID: 31542070
-
Development of pulmonary sarcoidosis in Crohn's disease patient under infliximab biosimilar treatment after long-term original infliximab treatment: a case report and literature review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Oct 12;21(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01948-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34641810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoidosis during infliximab therapy for Crohn's disease.J Dermatol. 2010 May;37(5):471-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2010.00861.x. J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20536653
-
Metastatic Crohn's disease despite infliximab therapy.An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 Suppl 1):104-106. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175713. An Bras Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 29267462 Free PMC article.
-
Use of infliximab and anti-infliximab antibody measurements to evaluate and optimize efficacy and safety of infliximab maintenance therapy in Crohn's disease.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4616. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651723 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 29;15(13):1658. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15131658. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis as a rare dermatologic manifestation of Crohn's disease mimicking cellulitis: a case report.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 29;20(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01371-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32727390 Free PMC article.
-
A Patient with KL-6 Elevation with Anti-TNFα Who Could Receive Long-Term Use without Interstitial Pneumonia after Class Switch of Anti-TNFα.Inflamm Intest Dis. 2019 May;4(1):35-40. doi: 10.1159/000497778. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Inflamm Intest Dis. 2019. PMID: 31172011 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced sarcoidosis in a patient treated with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist for hidradenitis suppurativa.JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Jun 6;4(6):543-545. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.03.007. eCollection 2018 Jul. JAAD Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29892670 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A case of leukocytoclastic vasculitis associated with anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2018 Jun;35(3):323-324. doi: 10.5114/ada.2018.76230. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2018. PMID: 30008655 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

