Confined diffusion of transmembrane proteins and lipids induced by the same actin meshwork lining the plasma membrane
- PMID: 26864625
- PMCID: PMC4814218
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E15-04-0186
Confined diffusion of transmembrane proteins and lipids induced by the same actin meshwork lining the plasma membrane
Abstract
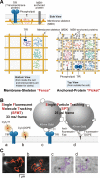
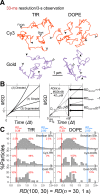
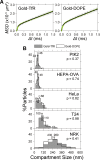
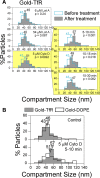
The mechanisms by which the diffusion rate in the plasma membrane (PM) is regulated remain unresolved, despite their importance in spatially regulating the reaction rates in the PM. Proposed models include entrapment in nanoscale noncontiguous domains found in PtK2 cells, slow diffusion due to crowding, and actin-induced compartmentalization. Here, by applying single-particle tracking at high time resolutions, mainly to the PtK2-cell PM, we found confined diffusion plus hop movements (termed "hop diffusion") for both a nonraft phospholipid and a transmembrane protein, transferrin receptor, and equal compartment sizes for these two molecules in all five of the cell lines used here (actual sizes were cell dependent), even after treatment with actin-modulating drugs. The cross-section size and the cytoplasmic domain size both affected the hop frequency. Electron tomography identified the actin-based membrane skeleton (MSK) located within 8.8 nm from the PM cytoplasmic surface of PtK2 cells and demonstrated that the MSK mesh size was the same as the compartment size for PM molecular diffusion. The extracellular matrix and extracellular domains of membrane proteins were not involved in hop diffusion. These results support a model of anchored TM-protein pickets lining actin-based MSK as a major mechanism for regulating diffusion.
© 2016 Fujiwara et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures


References
-
- Ayscough K. Use of latrunculin-A, an actin monomer-binding drug. Methods Enzymol. 1998;298:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Billaudeau C, Mailfert S, Trombik T, Bertaux N, Rouger V, Hamon Y, He HT, Marguet D. Probing the plasma membrane organization in living cells by spot variation fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 2013;519:277–302. - PubMed
-
- Bubb MR, Spector I, Beyer BB, Fosen KM. Effects of jasplakinolide on the kinetics of actin polymerization. An explanation for certain in vivo observations. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5163–5170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

