Femtosecond laser for cavity preparation in enamel and dentin: ablation efficiency related factors
- PMID: 26864679
- PMCID: PMC4750072
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20950
Femtosecond laser for cavity preparation in enamel and dentin: ablation efficiency related factors
Abstract
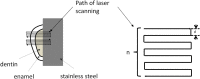
To study the effects of laser fluence (laser energy density), scanning line spacing and ablation depth on the efficiency of a femtosecond laser for three-dimensional ablation of enamel and dentin. A diode-pumped, thin-disk femtosecond laser (wavelength 1025 nm, pulse width 400 fs) was used for the ablation of enamel and dentin. The laser spot was guided in a series of overlapping parallel lines on enamel and dentin surfaces to form a three-dimensional cavity. The depth and volume of the ablated cavity was then measured under a 3D measurement microscope to determine the ablation efficiency. Different values of fluence, scanning line spacing and ablation depth were used to assess the effects of each variable on ablation efficiency. Ablation efficiencies for enamel and dentin were maximized at different laser fluences and number of scanning lines and decreased with increases in laser fluence or with increases in scanning line spacing beyond spot diameter or with increases in ablation depth. Laser fluence, scanning line spacing and ablation depth all significantly affected femtosecond laser ablation efficiency. Use of a reasonable control for each of these parameters will improve future clinical application.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effects of femtosecond laser on hard dental tissues: A scoping review.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Nov 20;39(1):286. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04225-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39567415
-
Femtosecond laser ablation of dentin and enamel: relationship between laser fluence and ablation efficiency.J Biomed Opt. 2015 Feb;20(2):28004. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.2.028004. J Biomed Opt. 2015. PMID: 25695161
-
[Effects of fluence and scanning velocity on the ablation efficiency of dentin and enamel by femtosecond laser].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 May;48(5):299-302. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2013.05.010. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24004627 Chinese.
-
Selectivity, efficiency, and surface characteristics of hard dental tissues ablated with ArF pulsed excimer lasers.Lasers Surg Med. 1991;11(6):499-510. doi: 10.1002/lsm.1900110603. Lasers Surg Med. 1991. PMID: 1753845
-
Why wavelength and delivery systems are the most important factors in using a dental hard-tissue laser: a literature review.Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2003 Nov;24(11):837-8, 841, 843 passim; quiz 848. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2003. PMID: 18624131 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced laser scanning for highly-efficient ablation and ultrafast surface structuring: experiment and model.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 26;8(1):17376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35604-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30478282 Free PMC article.
-
Focus Tracking System for Femtosecond Laser Machining using Low Coherence Interferometry.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 12;9(1):4167. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40749-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30862829 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of femtosecond laser on hard dental tissues: A scoping review.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Nov 20;39(1):286. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04225-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39567415
-
Femtosecond laser dentistry for precise and efficient cavity preparation in teeth.Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Aug 4;13(9):4559-4571. doi: 10.1364/BOE.463756. eCollection 2022 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 36187240 Free PMC article.
-
Highly-efficient laser ablation of copper by bursts of ultrashort tuneable (fs-ps) pulses.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 22;9(1):12280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48779-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31439881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rizoiu I., Kohanghadosh F., Kimmel A. I. & Eversole L. R. Pulpal thermal responses to an erbium, chromium: YSGG pulsed laser hydrokinetic system. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 86, 220–223 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Cavalcanti B. N., Otani C. & Rode S. M. High-speed cavity preparation techniques with different water flows. J. Prosthet. Dent. 87, 158–161 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Glockner K., Rumpler J., Ebeleseder K. & Städtler P. Intrapulpal temperature during preparation with the Er:YAG laser compared to the conventional burr: an in vitro study. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 16, 153–157 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Portillo M. M. et al.. Morphological alterations in dentine after mechanical treatment and ultrashort pulse laser irradiation. Lasers Med. Sci. 27, 53–58 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Luengo M. C. et al.. Evaluation of micromorphological changes in tooth enamel after mechanical and ultrafast laser preparation of surface cavities. Lasers Med. Sci. 28, 267–273 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

