Academic Achievement of Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Students in an ASL/English Bilingual Program
- PMID: 26864688
- PMCID: PMC4886322
- DOI: 10.1093/deafed/env072
Academic Achievement of Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Students in an ASL/English Bilingual Program
Abstract
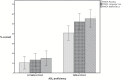
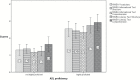
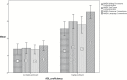
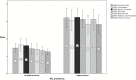
There has been a scarcity of studies exploring the influence of students' American Sign Language (ASL) proficiency on their academic achievement in ASL/English bilingual programs. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of ASL proficiency on reading comprehension skills and academic achievement of 85 deaf or hard-of-hearing signing students. Two subgroups, differing in ASL proficiency, were compared on the Northwest Evaluation Association Measures of Academic Progress and the reading comprehension subtest of the Stanford Achievement Test, 10th edition. Findings suggested that students highly proficient in ASL outperformed their less proficient peers in nationally standardized measures of reading comprehension, English language use, and mathematics. Moreover, a regression model consisting of 5 predictors including variables regarding education, hearing devices, and secondary disabilities as well as ASL proficiency and home language showed that ASL proficiency was the single variable significantly predicting results on all outcome measures. This study calls for a paradigm shift in thinking about deaf education by focusing on characteristics shared among successful deaf signing readers, specifically ASL fluency.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
American Sign Language/English bilingual model: a longitudinal study of academic growth.J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2013 Oct;18(4):532-44. doi: 10.1093/deafed/ent027. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2013. PMID: 23741074
-
American Sign Language and Academic English: Factors Influencing the Reading of Bilingual Secondary School Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students.J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2017 Jan;22(1):59-71. doi: 10.1093/deafed/enw065. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2017. PMID: 27789551
-
Superordinate Precision: An Examination of Academic Writing Among Bilingual Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students.J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2018 Apr 1;23(2):173-182. doi: 10.1093/deafed/enx052. J Deaf Stud Deaf Educ. 2018. PMID: 29228307
-
English Literacy Outcomes in Sign Bilingual Programs: Current State of the Knowledge.Am Ann Deaf. 2020;164(5):560-576. doi: 10.1353/aad.2020.0003. Am Ann Deaf. 2020. PMID: 32089536 Review.
-
The Effects of American Sign Language on English Reading Proficiency.Am Ann Deaf. 2023;167(5):745-760. doi: 10.1353/aad.2023.0010. Am Ann Deaf. 2023. PMID: 38661782
Cited by
-
Number Stroop Effects in Arabic Digits and ASL Number Signs: The Impact of Age and Setting of Language Acquisition.Lang Learn Dev. 2023;19(1):95-123. doi: 10.1080/15475441.2022.2047689. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Lang Learn Dev. 2023. PMID: 36844479 Free PMC article.
-
Preliteracy Skills in Young Children Who are Deaf/Hard of Hearing: Secondary Analysis of the Technology-assisted Language Intervention Randomized Trials.J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2025 Jul 17:10.1097/DBP.0000000000001394. doi: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000001394. Online ahead of print. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40700591 Free PMC article.
-
Deafness and early language deprivation influence arithmetic performances.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Nov 30;16:1000598. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.1000598. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36530200 Free PMC article.
-
Conversation Initiation in Families With a Toddler Who Is Deaf or Hard of Hearing.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2025 May 6;34(3):1256-1268. doi: 10.1044/2025_AJSLP-24-00254. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40227124
-
Does early exposure to spoken and sign language affect reading fluency in deaf and hard-of-hearing adult signers?Front Psychol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1145638. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1145638. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37799519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen T. E. (1994). Who are the deaf and hard-of-hearing students leaving high school and entering postsecondary education? Unpublished manuscript. Washington, DC: Gallaudet University Center for Assessment and Demographic Studies; Retrieved fromhttp://research.gallaudet.edu/AnnualSurvey/whodeaf.php
-
- Antia S. D. Jones P. B. Reed S., & Kreimeyer K. H (2009). Academic status and progress of deaf and hard-of-hearing students in general education classrooms. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 14, 293–311. doi:10.1093/deafed/enp009 - PubMed
-
- Arnesen K. Enerstvedt R. T. Engen E. A. Engen T. Hoie G., & Vonen A. M (2008). The linguistic milieu of Norwegian children with hearing loss. American Annals of the Deaf, 153, 65–77. doi:10.1353/aad.0.0000 - PubMed
-
- Cawthon S. (2004). Schools for the deaf and the No Child Left Behind Act. American Annals of the Deaf, 149, 314–323. doi:10.1353/aad.2005.0002 - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain C. (2002). Reading skills of deaf adults who sign: Good and poor readers compared (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). McGill University, Montreal, Québec, Canada: Retrieved from http://digitool.library.mcgill.ca/webclient/StreamGate?folder_id=0&dvs=1...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

