Comparison of the Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) and the modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS) in evaluating the prognosis of patients with operable and inoperable non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 26864695
- PMCID: PMC11819379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-015-2113-0
Comparison of the Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) and the modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS) in evaluating the prognosis of patients with operable and inoperable non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) and modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS) are shown to be reliable prognostic indexes in patients with operable and inoperable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Considering the difference between the two indexes lies in whether hypoalbuminemia without an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) is associated with worse survival, this study aims to evaluate the prognostic performance of hypoalbuminemia in patients without an elevated CRP and to compare the prognostic value of GPS and mGPS in patients with operable and inoperable NSCLC.
Methods: The data of 2988 patients were retrospectively collected from the Shanghai Health Information Network. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression was performed to investigate the prognostic effect of albumin, CRP, GPS and mGPS. Restricted cubic spline was also performed to evaluate the relationship between albumin and hazard ratio. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were estimated and compared using the log-rank test. Additional discriminative ability of GPS and of mGPS was evaluated using the area under the curve and Harrell's concordance index.
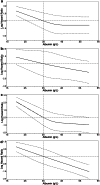
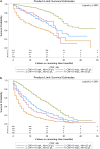
Results: Hypoalbuminemia was associated with worse survival in both operable and inoperable patients without an elevated CRP. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve of hypoalbuminemic patients without an elevated CRP was more close to the curve of patients with an elevated CRP and a normal albumin than to the curve of patients with neither of these abnormalities. Multivariate analysis, AUC and C-index all indicated that GPS had a higher prognostic value than mGPS.
Conclusions: Hypoalbuminemia was associated with worse survival in patients with or without an elevated CRP. GPS was superior to mGPS in predicting survival in operable and inoperable NSCLC patients.
Keywords: Albumin; C-reactive protein; Glasgow Prognostic Score; Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score; Non-small cell lung cancer; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Comparison of Glasgow prognostic score and prognostic index in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar;141(3):563-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1839-4. Epub 2014 Sep 26. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25257958 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Presence of Missing Data Affect the Performance of the SORG Machine-learning Algorithm for Patients With Spinal Metastasis? Development of an Internet Application Algorithm.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Jan 1;482(1):143-157. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002706. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37306629 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Radical radiotherapy for stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer in patients not sufficiently fit for or declining surgery (medically inoperable).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD002935. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002935. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 10;(3):CD002935. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002935.pub2. PMID: 11406051 Updated.
Cited by
-
Development of a Survival Prognostic Model for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 20;10:362. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00362. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32266143 Free PMC article.
-
Glasgow Prognostic Score predicts chemotherapy-triggered acute exacerbation-interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Mar;12(5):667-675. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13792. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33480111 Free PMC article.
-
A new prognostic score based on the systemic inflammatory response in patients with inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Aug 8;9:4879-86. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S107279. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27540301 Free PMC article.
-
Acute palliative care unit-initiated interventions for advanced cancer patients at the end of life: prediction of impending death based on Glasgow Prognostic Score.Support Care Cancer. 2021 Mar;29(3):1557-1564. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05638-z. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Support Care Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32734391
-
Predicting outcomes of Lung Cancer using the modified glasgow prognostic score: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(3Part-II):534-543. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.8397. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38356845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alifano M, Falcoz PE, Seegers V, Roche N, Schussler O, Younes M, Antonacci F, Forgez P, Dechartres A, Massard G, Damotte D, Régnard J (2011) Preresection serum C-reactive protein measurement and survival among patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 142(5):1161–1167 - PubMed
-
- Crumley AB, Stuart RC, McKernan M, McMillan DC (2010) Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer? World J Surg 34(10):2393–2398. doi:10.1007/s00268-010-0641-y - PubMed
-
- Dajczman E, Kasymjanova G, Kreisman H, Swinton N, Pepe C, Small D (2008) Should patient-rated performance status affect treatment decisions in advanced lung cancer? J Thorac Oncol 3(10):1133–1136. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318186a272 - PubMed
-
- DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44(3):837–845 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

