Circulating Endothelial Cells and Endothelial Function Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events and Early Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 26864952
- PMCID: PMC4842320
- DOI: 10.1111/joic.12269
Circulating Endothelial Cells and Endothelial Function Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events and Early Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
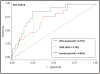
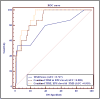
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and circulating endothelial cells (CECs) are mobilized from the bone marrow and increase in the early phase after ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The aim of this study was to assess the prognostic significance of CECs and indices of endothelial dysfunction in patients with STEMI. In 78 patients with acute STEMI, characterization of CD34+/VEGFR2+CECs, and indices of endothelial damage/dysfunction such as brachial artery flow mediated dilatation (FMD) were determined. Blood samples for CECs assessment and quantification were obtained within 24 hours of admission and FMD was assessed during the index hospitalization. At 30 days follow up, the primary composite end point of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) consisting of all-cause mortality, recurrent nonfatal MI, or heart failure and the secondary endpoint of early adverse left ventricular (LV) remodeling were analyzed. The 17 patients (22%) who developed MACE had significantly higher CEC level (P = 0.004), von Willebrand factor (vWF) level (P = 0.028), and significantly lower FMD (P = 0.006) compared to the remaining patients. Logistic regression analysis showed that CECs level and LV ejection fraction were independent predictors of MACE. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) for CEC level, FMD, and the logistic model with both markers were 0.73, 0.75, and 0.82, respectively, for prediction of the MACE. The 16 patients who developed the secondary endpoint had significantly higher CEC level compared to remaining patients (P = 0.038). In conclusion, increased circulating endothelial cells and endothelial dysfunction predicted the occurrence of major adverse cardiac events and adverse cardiac remodeling in patients with STEMI.
© 2016, Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognosis-based definition of left ventricular remodeling after ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Eur Radiol. 2019 May;29(5):2330-2339. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5875-3. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30547201 Free PMC article.
-
Combined assessment of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and ejection fraction by left ventriculography predicts long-term outcomes of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Heart Vessels. 2018 May;33(5):453-461. doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-1080-6. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Heart Vessels. 2018. PMID: 29143103
-
Adverse diastolic remodeling after reperfused ST-elevation myocardial infarction: An important prognostic indicator.Am Heart J. 2016 Oct;180:117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.05.020. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Am Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27659890
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Circulating endothelial cells in cardiovascular disease.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Oct 17;48(8):1538-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.02.078. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 17045885 Review.
Cited by
-
The Intriguing Relationships of von Willebrand Factor, ADAMTS13 and Cardiac Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021 Sep 15;8(9):115. doi: 10.3390/jcdd8090115. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021. PMID: 34564132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cells and blood vessels are major targets for COVID-19-induced tissue injury and spreading to various organs.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 21;28(3):275-289. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.275. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35110950 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microvesicles containing microRNAs in vascular endothelial dysfunction.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):7933-7945. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14716. Epub 2019 Oct 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31576661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronary microvascular injury in myocardial infarction: perception and knowledge for mitochondrial quality control.Theranostics. 2021 May 3;11(14):6766-6785. doi: 10.7150/thno.60143. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34093852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale: early and long-term effects on endothelial function after percutaneous occlusion procedure.Heart Vessels. 2019 Sep;34(9):1499-1508. doi: 10.1007/s00380-019-01385-2. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Heart Vessels. 2019. PMID: 30895384
References
-
- Massa M, Rosti V, Ferrario M, Campanelli R, Ramajoli I, Rosso R, De Ferrari G, Ferlini M, Goffredo L, Bertoletti A, Klersy C, Pecci A, RemigioMoratti R, Tavazzi L. Increased circulating hematopoieticand endothelial progenitor cells in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. Blood. 2005;105:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Shintani S, Murohara T, Ikeda H, Ueno T, Honma T, Katoh A, Sasaki K, Shimada T, Oike Y, Imaizumi T. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;103:2776–2779. - PubMed
-
- Wojakowski W, Tendera M, Michalowska A, Majka M, Kucia M, Maslankiewicz K, Wyderka R, Ochala A, Ratajczak MZ. Mobilization ofCD34/CXCR4+, CD34/CD117+, c-met+ stem cells, and mononuclearcells expressing early cardiac, muscle, and endothelial markers into peripheral blood in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;110:3213–3220. - PubMed
-
- Badorff C, Brandes RP, Popp R, Rupp S, Urbich C, Aicher A, Fleming I, Busse R, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Transdifferentiation of blood-derived human adult endothelial progenitor cells into functionally active cardiomyocytes. Circulation. 2003;107:1024–1032. - PubMed
-
- Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, Köstering M, Hernandez A, Sorg RV, Kögler G, Wernet P. Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation. 2002;106:1913–1918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
