Multifunctional flexible free-standing titanate nanobelt membranes as efficient sorbents for the removal of radioactive (90)Sr(2+) and (137)Cs(+) ions and oils
- PMID: 26865116
- PMCID: PMC4750037
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20920
Multifunctional flexible free-standing titanate nanobelt membranes as efficient sorbents for the removal of radioactive (90)Sr(2+) and (137)Cs(+) ions and oils
Abstract
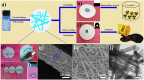
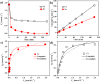
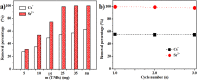
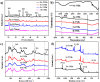
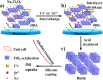
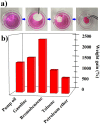
For the increasing attention focused on saving endangered environments, there is a growing need for developing membrane materials able to perform complex functions such as removing radioactive pollutants and oil spills from water. A major challenge is the scalable fabrication of membranes with good mechanical and thermal stability, superior resistance to radiation, and excellent recyclability. In this study, we constructed a multifunctional flexible free-standing sodium titanate nanobelt (Na-TNB) membrane that was assembled as advanced radiation-tainted water treatment and oil uptake. We compared the adsorption behavior of (137)Cs(+) and (90)Sr(2+) on Na-TNB membranes under various environmental conditions. The maximum adsorption coefficient value (Kd) for Sr(2+) reaches 10(7) mL g(-1). The structural collapse of the exchange materials were confirmed by XRD, FTIR and XPS spectroscopy as well as Raman analysis. The adsorption mechanism of Na-TNB membrane is clarified by forming a stable solid with the radioactive cations permanently trapped inside. Besides, the engineered multilayer membrane is exceptionally capable in selectively and rapidly adsorbing oils up to 23 times the adsorbent weight when coated with a thin layer of hydrophobic molecules. This multifunctional membrane has exceptional potential as a suitable material for next generation water treatment and separation technologies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium-copper hexacyanoferrate-functionalized magnetic nanoclusters for the highly efficient magnetic removal of radioactive caesium from seawater.Water Res. 2017 Nov 15;125:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.037. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Water Res. 2017. PMID: 28834769
-
Molten salt mediated single-step synthesis of reusable nanostructured CaTiO3 for the removal and recovery of Sr2+: A potential adsorbent for the contaminated water bodies.Environ Res. 2024 Jun 1;250:118486. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118486. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38365057
-
The use of clinoptilolite and its sodium form for removal of radioactive cesium, and strontium from nuclear wastewater and Pb2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, Ba2+ from municipal wastewater.Appl Radiat Isot. 1999 Apr;50(4):655-60. doi: 10.1016/s0969-8043(98)00134-1. Appl Radiat Isot. 1999. PMID: 10101831
-
Titanate-based adsorbents for radioactive ions entrapment from water.Nanoscale. 2013 Mar 21;5(6):2232-42. doi: 10.1039/c3nr33622k. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 23412572 Review.
-
Magnetic hybrid gels for emulsified oil adsorption: an overview of their potential to solve environmental problems associated to petroleum spills.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jan;27(1):861-872. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06752-0. Epub 2019 Dec 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31814073 Review.
Cited by
-
Facile Synthesis of Porous Polymer Using Biomass Polyphenol Source for Highly Efficient Separation of Cs+ from Aqueous Solution.Sci Rep. 2020 May 19;10(1):8221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65099-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32427956 Free PMC article.
-
Free-Standing Sodium Titanate Ultralong Nanotube Membrane with Oil-Water Separation, Self-Cleaning, and Photocatalysis Properties.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020 Jan 28;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s11671-020-3255-9. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020. PMID: 31993805 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethersulfone Blended with Titanium Dioxide Nanoribbons/Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes for Strontium Removal from Water.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 29;14(7):1390. doi: 10.3390/polym14071390. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ge J. et al. Pumping through porous hydrophobic/oleophilic materials: an alternative technology for oil spill remediation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 126, 3686–3690 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Buesseler K., Aoyama M. & Fukasawa M. Impacts of the fukushima nuclear power plants on marine radioactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 9931–9935 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Li N. et al. Highly efficient, irreversible and selective ion exchange property of layered titanate nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 835–841 (2012).
-
- Yuan S., Peng D. H., Song D. D. & Gong J. M. Layered titanate nanosheets as an enhanced sensing platform for ultrasensitive stripping voltammetric detection of mercury(II). Sensors Actuat. B-Chem. 181, 432–438 (2013).
-
- International atomic energy agency (IAEA), technical reports series no 408, applications of ion exchange process for the treatment of radioactive waste and management of spent ion exchangers, Vienna (2002).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

