Dexmedetomidine post-treatment induces neuroprotection via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rats with subarachnoid haemorrhage
- PMID: 26865131
- PMCID: PMC4748945
- DOI: 10.1093/bja/aev549
Dexmedetomidine post-treatment induces neuroprotection via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rats with subarachnoid haemorrhage
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine, a sedative agent, provides neuroprotection when administered during or before brain ischaemia. This study was designed to determine whether dexmedetomidine post-treatment induces neuroprotection against subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) and the mechanisms for this effect.
Methods: Subarachnoid haemorrhage was induced by endovascular perforation to the junction of the right middle and anterior cerebral arteries in adult rats. Dexmedetomidine was applied immediately or 2 h after onset of SAH. Neurological outcome was evaluated 2 days after SAH. Right frontal cortex area 1 was harvested 24 h after SAH for western blotting.
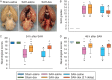
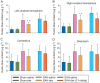
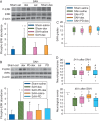
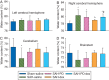
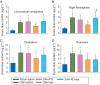
Results: Subarachnoid haemorrhage reduced neurological scores and increased brain oedema and blood-brain barrier permeability. These effects were attenuated by dexmedetomidine post-treatment. Neuroprotection by dexmedetomidine was abolished by PD98095, an inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. Phospho-ERK, the activated form of ERK, was increased by dexmedetomidine; this activation was inhibited by PD98095.
Conclusions: Dexmedetomidine post-treatment provides neuroprotection against SAH. This effect appears to be mediated by ERK.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; post-treatment; subarachnoid haemorrhage.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Journal of Anaesthesia. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Venti M. Subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhage. Front Neurol Neurosci 2012; 30: 149–53 - PubMed
-
- Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, van Gijn J. Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke 1997; 28: 660–4 - PubMed
-
- Ingall TJ, Whisnant JP, Wiebers DO, O'Fallon WM. Has there been a decline in subarachnoid hemorrhage mortality? Stroke 1989; 20: 718–24 - PubMed
-
- Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of α2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology 2000; 93: 1345–9 - PubMed
-
- Walker SM, Howard RF, Keay KA, Fitzgerald M. Developmental age influences the effect of epidural dexmedetomidine on inflammatory hyperalgesia in rat pups. Anesthesiology 2005; 102: 1226–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

