Calcium and Magnesium Ions Are Membrane-Active against Stationary-Phase Staphylococcus aureus with High Specificity
- PMID: 26865182
- PMCID: PMC4749956
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20628
Calcium and Magnesium Ions Are Membrane-Active against Stationary-Phase Staphylococcus aureus with High Specificity
Abstract
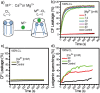
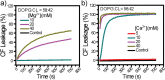
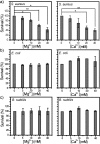
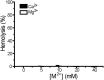
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is notorious for its ability to acquire antibiotic-resistance, and antibiotic-resistant S. aureus has become a wide-spread cause of high mortality rate. Novel antimicrobials capable of eradicating S. aureus cells including antibiotic-resistant ones are thus highly desired. Membrane-active bactericides and species-specific antimicrobials are two promising sources of novel anti-infective agents for fighting against bacterial antibiotic-resistance. We herein show that Ca(2+) and Mg(2+), two alkaline-earth-metal ions physiologically essential for diverse living organisms, both disrupt model S. aureus membranes and kill stationary-phase S. aureus cells, indicative of membrane-activity. In contrast to S. aureus, Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis exhibit unaffected survival after similar treatment with these two cations, indicative of species-specific activity against S. aureus. Moreover, neither Ca(2+) nor Mg(2+) lyses mouse red blood cells, indicative of hemo-compatibility. This works suggests that Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) may have implications in targeted eradication of S. aureus pathogen including the antibiotic-resistant ones.
Figures
References
-
- Moore C. E., Segal S., Berendt A. R., Hill A. V. S. & Day N. P. J. Lack of association between toll-like receptor 2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to severe disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 11, 1194–1197, doi: 10.1128/Cdli.11.6.1194-1197.2004 (2004). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wertheim H. F. L. & Verbrugh H. A. Global prevalence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 368, 1866 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013. Report by the U.S. Centers for Dieseas Control and Prevention.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

