LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA attenuates P2X7 receptor expression and inflammatory cytokine production induced by combined high glucose and free fatty acids in PC12 cells
- PMID: 26865268
- PMCID: PMC4854842
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-016-9500-0
LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA attenuates P2X7 receptor expression and inflammatory cytokine production induced by combined high glucose and free fatty acids in PC12 cells
Abstract
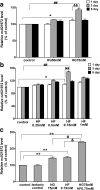
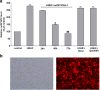
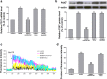
Diabetic neuropathy (DNP) is a frequent chronic complication of diabetes mellitus with potentially life-threatening outcomes. High glucose and elevated free fatty acids (FFAs) have been recently recognized as major causes of nervous system damage in diabetes. Our previous study has indicated extracellular stimuli, such as high glucose and/or FFA stress, may activate the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway and induce a p38 MAPK-dependent sensitization of the P2X7 receptor and release of inflammatory factors in PC12 cells, while the mechanisms underlying remain to be elucidated. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in diverse biological processes, including activation of a series of pathway signalings. Here, we showed combined high D-glucose and FFAs (HGHF) induced an increment of lncRNA-NONRATT021972 (NONCODE ID, nc021972) in PC12 cells. Nc021972 small interference RNA (siRNA) alleviated HGHF-induced activation of p38 MAPK, expression of the P2X7 receptor, and [Ca(2+)]i increment upon P2X7 receptor activation. Further experiments showed that there existed a crosstalk between nc021972 and the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling decreased nc021972-induced expression of the P2X7 receptor and [Ca(2+)]i increment upon P2X7 receptor activation. Also, nc021972 siRNA inhibited HGHF-induced PC12 release of TNF-α and IL-6 and rescued decreased cell viability mediated by the P2X7 receptor. Therefore, inhibition of nc021972 may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy for diabetes complicated with nervous inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Diabetic neuropathy; High fatty acids; High glucose; Long noncoding RNA; P2X7 receptor; PC12 cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NONRATT021972 long-noncoding RNA: A promising lncRNA in diabetes-related diseases.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 2;16(6):902-908. doi: 10.7150/ijms.34200. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trans-resveratrol attenuates high fatty acid-induced P2X7 receptor expression and IL-6 release in PC12 cells: possible role of P38 MAPK pathway.Inflammation. 2015 Feb;38(1):327-37. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-0036-6. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25348860
-
High fatty acids modulate P2X(7) expression and IL-6 release via the p38 MAPK pathway in PC12 cells.Brain Res Bull. 2013 May;94:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23438872
-
LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA regulates neuropathic pain behaviors in type 2 diabetic rats through the P2X7 receptor in dorsal root ganglia.Mol Brain. 2016 Apr 23;9:44. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0226-2. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27107575 Free PMC article.
-
Long non coding RNAs involved in MAPK pathway mechanism mediates diabetic neuropathic pain.Cell Biol Int. 2020 Dec;44(12):2372-2379. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11457. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Cell Biol Int. 2020. PMID: 32844535 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Foot Ulcers.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Jun 9;14:2549-2560. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S310566. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34135607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances with Long Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Apr 30;13:1429-1434. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S249232. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32431526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional roles of lncRNAs and its potential mechanisms in neuropathic pain.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 May 15;11(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0671-8. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31092294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NONRATT021972 long-noncoding RNA: A promising lncRNA in diabetes-related diseases.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 2;16(6):902-908. doi: 10.7150/ijms.34200. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Big Entity of New RNA World: Long Non-Coding RNAs in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 4;9:300. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00300. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29915562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carroll SL, Byer SJ, Dorsey DA, Watson MA, Schmidt RE. Ganglion-specific patterns of diabetes-modulated gene expression are established in prevertebral and paravertebral sympathetic ganglia prior to the development of neuroaxonal dystrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63:1144–1154. doi: 10.1093/jnen/63.11.1144. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

