Triazine-Based Sequence-Defined Polymers with Side-Chain Diversity and Backbone-Backbone Interaction Motifs
- PMID: 26865312
- PMCID: PMC4804744
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201509864
Triazine-Based Sequence-Defined Polymers with Side-Chain Diversity and Backbone-Backbone Interaction Motifs
Abstract
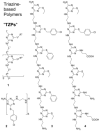
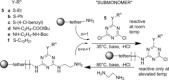
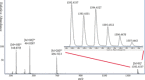
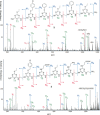
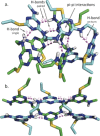
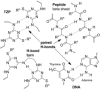
Sequence control in polymers, well-known in nature, encodes structure and functionality. Here we introduce a new architecture, based on the nucleophilic aromatic substitution chemistry of cyanuric chloride, that creates a new class of sequence-defined polymers dubbed TZPs. Proof of concept is demonstrated with two synthesized hexamers, having neutral and ionizable side chains. Molecular dynamics simulations show backbone-backbone interactions, including H-bonding motifs and pi-pi interactions. This architecture is arguably biomimetic while differing from sequence-defined polymers having peptide bonds. The synthetic methodology supports the structural diversity of side chains known in peptides, as well as backbone-backbone hydrogen-bonding motifs, and will thus enable new macromolecules and materials with useful functions.
Keywords: biomimetics; macromolecules; sequence-defined polymers; simulations; solid-phase synthesis.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- None
-
- Sequence-Controlled Polymers: Synthesis Self-Assembly, and Properties, Vol. 1170, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C., 2014;
-
- Lutz J.-F., Ouchi M., Liu D. R., Sawamoto M., Science 2013, 341, 1238149; - PubMed
-
- Stayshich R. M., Weiss R. M., Li J., Meyer T. Y., Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 220–225; - PubMed
-
- Norris B. N., Zhang S., Campbell C. M., Auletta J. T., Calvo-Marzal P., Hutchison G. R., Meyer T. Y., Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1384–1392;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

