Anti-PD-1 Inhibitor-Related Pneumonitis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26865455
- PMCID: PMC4818710
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0267
Anti-PD-1 Inhibitor-Related Pneumonitis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
The recent approval of two PD-1 inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has rapidly led to the widespread use of these agents in oncology practices. Pneumonitis has been recognized as a potentially life-threatening adverse event among NSCLC patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors; however, the detailed clinical and radiographic manifestations of this entity remain to be described. We report on two cases of anti-PD-1 pneumonitis in advanced NSCLC patients treated with nivolumab after its FDA approval. Both patients presented with ground-glass and reticular opacities and consolidations in a peripheral distribution on CT, demonstrating a radiographic pattern of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Consolidations were extensive and rapidly developed within 8 weeks of therapy in both cases. Both patients were treated with corticosteroids with subsequent improvement of respiratory symptoms and radiographic findings. One patient experienced recurrent pneumonitis after completing corticosteroid taper, or a "pneumonitis flare," in the absence of nivolumab retreatment, with subsequent improvement upon corticosteroid readministration. With the increasing use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in a growing number of tumor types, awareness of the radiographic and clinical manifestations of PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis will be critical for the prompt diagnosis and management of this potentially serious adverse event.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Nishino: Consultant, Bristol-Myers Squibb
Hodi: Consultant to Merck, Genentech, and Novartis.
Awad: Consultant to Merck, Genentech, and AstraZeneca
Figures
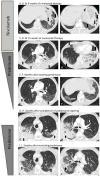
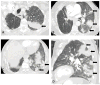
References
-
- Gettinger SN, Horn L, Gandhi L, et al. Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety of Nivolumab (Anti-Programmed Death 1 Antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2015;33(18):2004–12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3708. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rizvi NA, Mazieres J, Planchard D, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. The Lancet. Oncology. 2015;16(3):257–65. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70054-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

