Rapid Urine LAM Testing Improves Diagnosis of Expectorated Smear-Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis in an HIV-endemic Region
- PMID: 26865526
- PMCID: PMC4750056
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19992
Rapid Urine LAM Testing Improves Diagnosis of Expectorated Smear-Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis in an HIV-endemic Region
Abstract
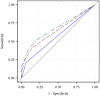
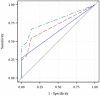
We sought to determine if urine lipoarabinomannan (LAM) would improve diagnosis of pulmonary TB. We enrolled consecutive adults presenting with ≥2 TB-related symptoms, obtained one induced sputum sample for smear microscopy (AFB) and mycobacterial culture, and performed urine LAM testing (Determine(TM) TB LAM, Alere). We used culture-confirmed pulmonary TB as the gold standard, and compared accuracy with area under receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROC). Among 90 participants, 82 of 88 tested (93%) were HIV-infected with a median CD4 168/mm(3) (IQR 89-256/mm(3)). Diagnostic sensitivities of urine LAM and sputum AFB were 42.1% (95% CI 29.1-55.9%) and 21.1% (95% CI 11.4-33.9%), and increased to 52.6% (95% CI 39.0-66.0%) when combined. Sensitivity of LAM increased significantly among participants with a lower Karnofsky Performance score, anemia, hypoalbuminemia, and higher C-reactive protein. Combining LAM with AFB had an AUROC = 0.68 (95% CI 0.59-0.77), significantly better than AFB alone (AUROC=0.58; 95% CI 0.51-0.64). The combination of LAM and AFB was significantly better than AFB alone among patients with Karnofsky Performance score ≤90, hemoglobin ≤10 g/dL, albumin ≤25 g/L, C-reactive protein ≥25 mg/L, or CD4 <200/mm(3). Urine LAM testing may be most beneficial among patients with functional impairment, elevated inflammatory markers, or greater immunosuppression.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Treatment of tuberculosis: Guidelines – 4th edition. Geneva: World Health Organization (2010). - PubMed
-
- Stop TB Program, World Health Organization. Reach the 3 million. Geneva: World Health Organization (2014).
-
- World Health Organization. Systematic screening for active tuberculosis: principles and recommendations. Geneva: World Health Organization (2013). - PubMed
-
- Lawn S. D. et al.. Urine lipoarabinomannan assay for tuberculosis screening before antiretroviral therapy diagnostic yield and association with immune reconstitution disease. AIDS. 23, 1875–1880 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

