Aβ40 Reduces P-Glycoprotein at the Blood-Brain Barrier through the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway
- PMID: 26865616
- PMCID: PMC4748076
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0350-15.2016
Aβ40 Reduces P-Glycoprotein at the Blood-Brain Barrier through the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway
Abstract
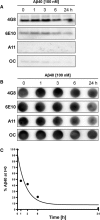
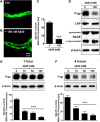
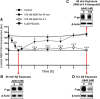
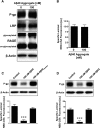
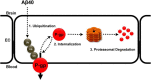
Failure to clear amyloid-β (Aβ) from the brain is in part responsible for Aβ brain accumulation in Alzheimer's disease (AD). A critical protein for clearing Aβ across the blood-brain barrier is the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in the luminal plasma membrane of the brain capillary endothelium. P-gp is reduced at the blood-brain barrier in AD, which has been shown to be associated with Aβ brain accumulation. However, the mechanism responsible for P-gp reduction in AD is not well understood. Here we focused on identifying critical mechanistic steps involved in reducing P-gp in AD. We exposed isolated rat brain capillaries to 100 nm Aβ40, Aβ40, aggregated Aβ40, and Aβ42. We observed that only Aβ40 triggered reduction of P-gp protein expression and transport activity levels; this occurred in a dose- and time-dependent manner. To identify the steps involved in Aβ-mediated P-gp reduction, we inhibited protein ubiquitination, protein trafficking, and the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and monitored P-gp protein expression, transport activity, and P-gp-ubiquitin levels. Thus, exposing brain capillaries to Aβ40 triggers ubiquitination, internalization, and proteasomal degradation of P-gp. These findings may provide potential therapeutic targets within the blood-brain barrier to limit P-gp degradation in AD and improve Aβ brain clearance.
Significance statement: The mechanism reducing blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. In the present study, we focused on defining this mechanism. We demonstrate that Aβ40 drives P-gp ubiquitination, internalization, and proteasome-dependent degradation, reducing P-gp protein expression and transport activity in isolated brain capillaries. These findings may provide potential therapeutic avenues within the blood-brain barrier to limit P-gp degradation in Alzheimer's disease and improve Aβ brain clearance.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; P-glycoprotein; blood–brain barrier; transporter; ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/361930-12$15.00/0.
Figures



References
-
- Beccano-Kelly DA, Kuhlmann N, Tatarnikov I, Volta M, Munsie LN, Chou P, Cao LP, Han H, Tapia L, Farrer MJ, Milnerwood AJ. Synaptic function is modulated by LRRK2 and glutamate release is increased in cortical neurons of G2019S LRRK2 knock-in mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:301. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
